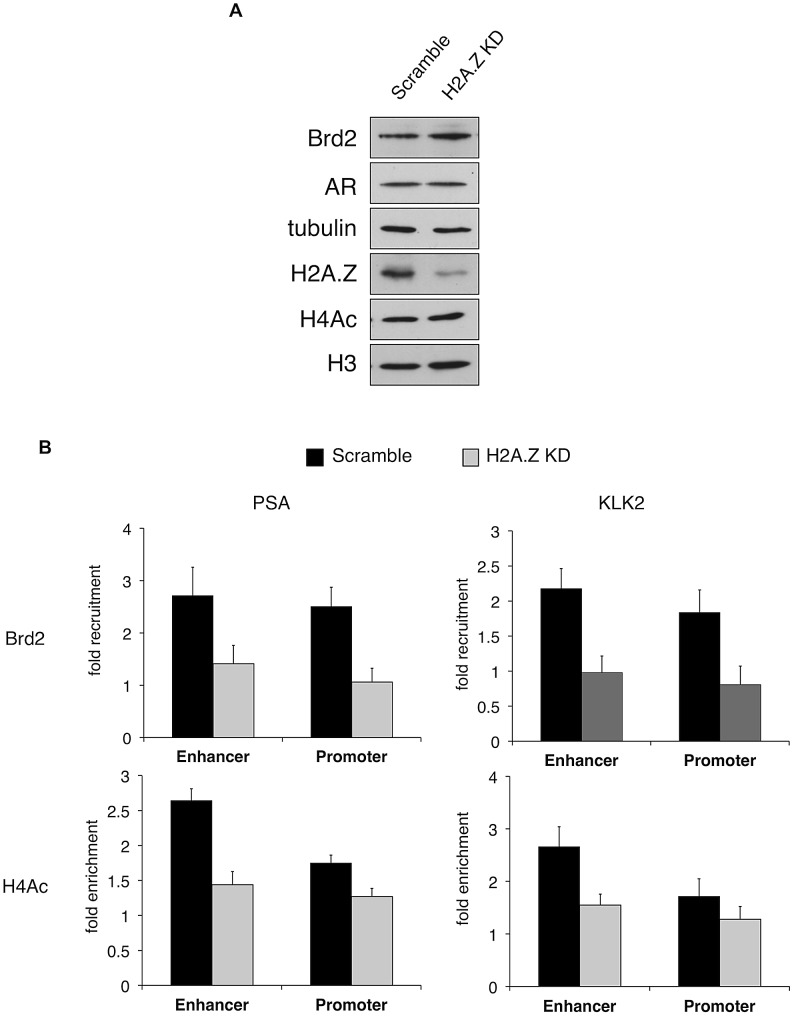
Figure 6. H2A.Z influences H4 acetylation and Brd2 recruitment at AR–regulated genes.
A. Western blot analyses of whole-cell lysates from LNCaP cells stably expressing either a scrambled control shRNA or an shRNA targeting H2A.Z-1 mRNA. H2A.Z knockdown does not significantly affect the protein levels of AR or Brd2, nor does it reduce global levels of tetra-acetylated H4 (H4Ac). Tubulin and H3 are shown for the purpose of loading controls. B. ChIP analysis of Brd2 and tetra-acetylated H4 at the PSA and KLK2 genes. Knockdown of H2A.Z reduces the recruitment of Brd2 as well as the acetylation of H4 at AR-regulated genes following hormone stimulation for 60 minutes. The data represent the fold-enrichment in hormone-stimulated cells relative to respective ethanol-treated controls (vehicle control). H4Ac ChIP was also normalized to H3 to account for changes in nucleosome density. Each qPCR reaction was performed in triplicate with each experiment repeated at least three times independently. Values are presented as means, ± standard deviation.