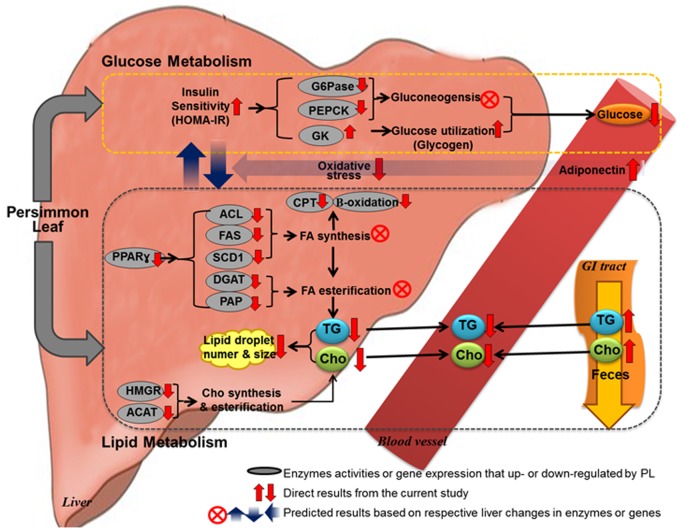
Figure 4. Proposed mechanism of PL on the glucose and lipid lowering action in C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice.
PL improved HOMA-IR, which may activate glucokinase activity and its mRNA expression and inhibit gluconeogenic enzymes activity in the liver, resulting in lowered blood glucose level. The enhanced hepatic insulin sensitivity may be related to the improved hepatic steatosis and dyslipidemia, since PL led to lower plasma and hepatic lipid levels via reduction of transcription factor PPARγ, lipogenic gene expression and enzyme activity with a simultaneous increase in fecal lipids excretion. Furthermore, PL ameliorated oxidative stress and increased adiponectin secretion, which may be also associated with improved insulin sensitivity, hepatic steatosis and dyslipidemia. ACAT; acyl CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase, ACL; ATP-citrate lyase, Cho; cholesterol, CPT; carnitine palmitoyl transferase, DGAT; glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, FA; fatty acid, FAS; fatty acid synthase, G6Pase; glucose-6-phosphatase, GK; glucokinase, GI tract; gastrointestinal tract, HMGR; 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme, HOMA-IR; homeostatic index of insulin resistance, PAP; phosphatidate phosphohydrolase, PL; powdered persimmon leaf, PEPCK; phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, PPARγ; peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ, SCD1; steraroyl-CoA desaturase-1, TG; triglyceride.