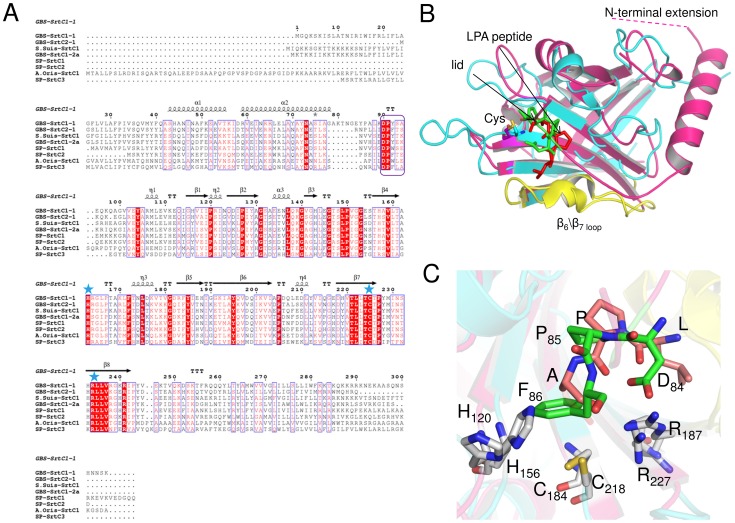
Figure 2. Structural comparison of GBS PI-1 SrtC2 crystal structure with S. aureus SrtA NMR structure.
(A) Multiple sequence alignment of the pilus-forming sortases crystallized so far. Structure-based sequence alignment of the GBS PI-1 SrtC2, SrtC1, GBS PI-2a SrtC1 (PDB 3O0P), S. pneumoniae sortase C1 (PDB 2W1J), sortase C2 (PDB 3G69), sortase C3 (PDB 2W1K), S. suis SrtC1 (PDB 3RE9) and A. oris SrtC1 (PDB 2XWG). Identical residues are shown with a red background, whereas similar residues are shown in red and highlighted with blue boxes. Residues located within the active site cleft are conserved among all sortases and are highlighted with blue stars, whereas the lid residues DPF\Y\W are highlighted with a purple box (http://espript.ibcp.fr/ESPript/ESPript/). (B) Superposition of GBS PI-1 SrtC2 (pink) with the S. aureus SrtA (cyan, PDB 2KID) in complex with the sorting signal analogue LPAT* (red). The β6/β7 loops are colored in yellow. Unique structural features of SrtC enzymes are the N-terminal extension and the flexible lid (with the DPF motif in green as stick representation). The catalytic cysteine residues are highlighted in yellow and shown in a stick representation. The apo-SrtC2 structure overlaps with the structure of peptide-bound SrtA with an overall Ca rmsd of 2.33 Å for 118 aligned residues. (C) The lid residues DPF (color, Asp84, Pro85, Phe86) of GBS pilus-forming sortase is located analogously to the LPA substrate peptide (shown in sticks where carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms, are depicted as white, red, and blue, respectively) in the structure of SrtA.