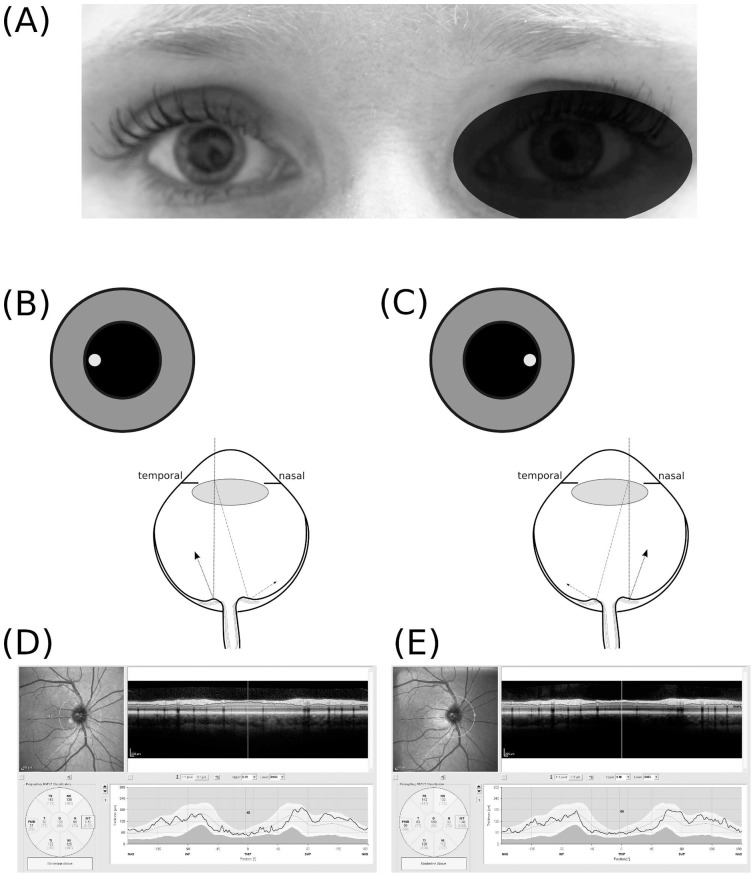
Figure 1. Off centre placement of the measurement beam.
(A) The OCT measurement beam is focused on the dilated right eye of subject #1, (B) temporal off–axis placement of the measurement beam results in a shorter light path to the temporal part of the optic nerve head (dotted line) and a longer pathway from the nasal part of the optic nerve head (dotted-dashed line). The difference in path length results in a tilted appearance of the B–scan. (C) Nasal off–axis placement of themeasurement beam results in a mirror pattern. The resulting averaged OCT image is of good quality (ART 25, signal strength 35 dB) for both (D) temporal off–axis placement and (E) nasal off–axis placement. The quantification of the RNFL thickness by the algorithm is however clearly different (Global average OD with temporal off-axis placement 106 μm and nasal off–axis placement 103 μm).