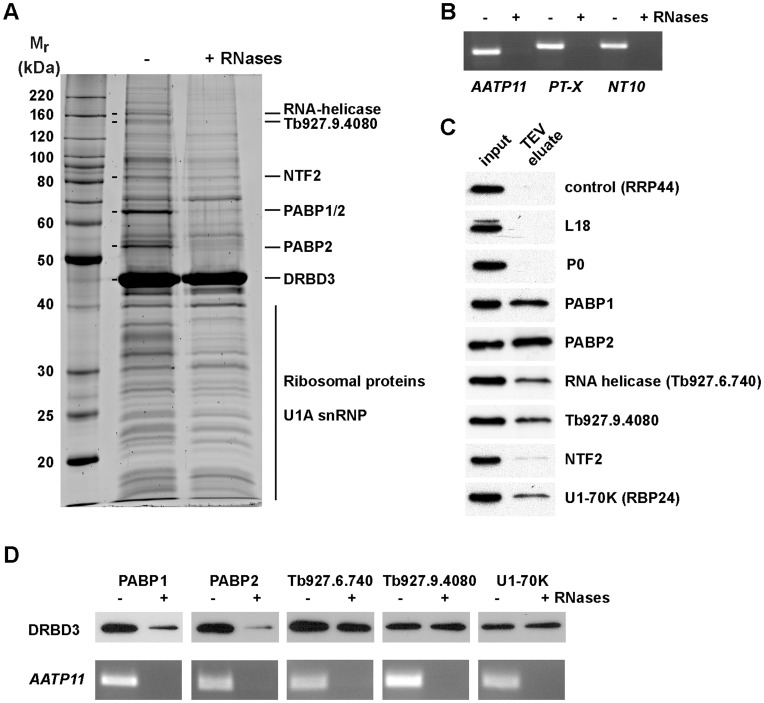
Figure 2. Identification of DRBD3-associated proteins by tandem-affinity purification (TAP).
(A) Protein extracts were obtained from cells expressing a TAP-DRBD3 fusion from the endogenous locus. The lysate was split into two halves, and RNAses A and T1 were added to one. Both fractions were processed in parallel for TAP as described in Materials and Methods. (B) The efficiency of the RNAses treatment was assessed by RT-PCR of the purified material after TEV protease incubation using oligonucleotides specific for transcripts known to be bound to DRBD3. (C) Protein interactions were confirmed by generating cell lines expressing TAP- or PTP-tagged versions of some of the identified protein partners. The presence of DRBD3 was assayed in the purified material by western blot analysis after IgG chromatography and TEV protease incubation. Ribosomes were pulled down using either L18 or P0 ribosomal proteins as baits. (D) To assess whether the observed protein interactions were RNA-dependent, lysates obtained from cell lines expressing TAP- or PTP-tagged versions of the indicated proteins were treated with RNAses A and T1 as indicated above. The presence of DRBD3 was assayed in the TEV eluates as in panel C, and the efficiency of the RNases treatment was evaluated by RT-PCR using oligonucleotides specific for the DRBD3-bound transcript AATP11 as above.