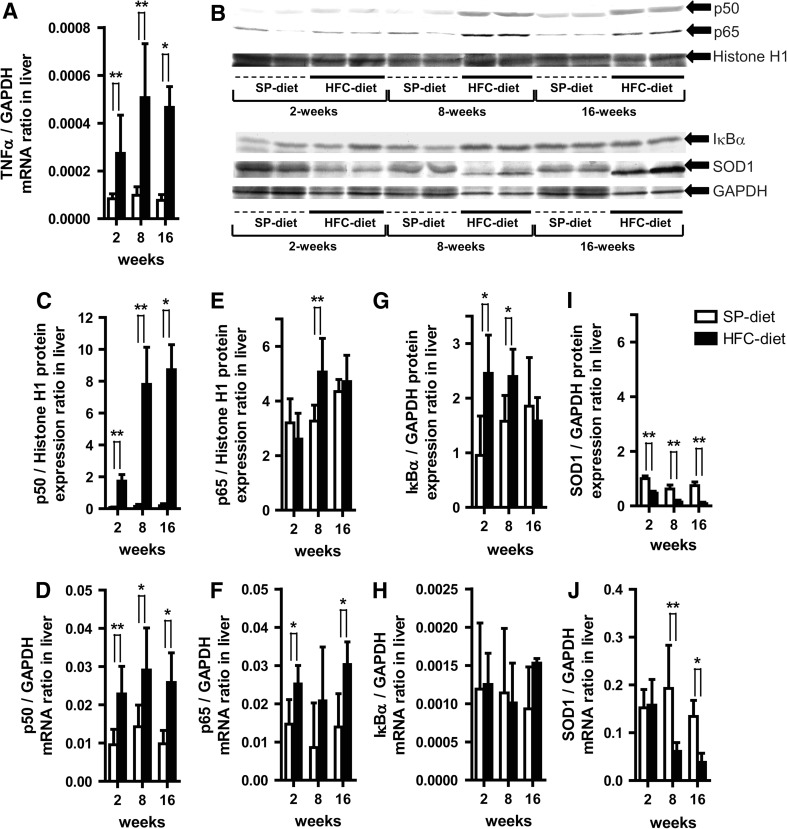
Fig. 1.
Effects of a high-fat and high-cholesterol-containing diet (HFC-diet) on hepatic tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), nuclear factor κB (p50/p65), inhibitor of κBα (IκBα), Cu2+/Zn2+-superoxide dismutase (SOD1) protein and their mRNA expressions. a TNF-α mRNA expression ratio. b Western blot results of respective protein expressions in whole liver tissue homogenates or nuclear fractions. c, d Hepatic p50 protein (c) and mRNA expression (d) ratios. e, f Hepatic p65 protein (e) and mRNA expression (f) ratios. g, h Hepatic IκBα protein (g) and mRNA expression (h) ratios. i, j Hepatic SOD1 protein (i) and mRNA expression (j) ratios. Each histogram represents a mean ratio ± standard deviation (SD). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, compared with the stroke-prone control chow-fed diet (SP-diet) group within each diet–treatment period. GAPDH Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase