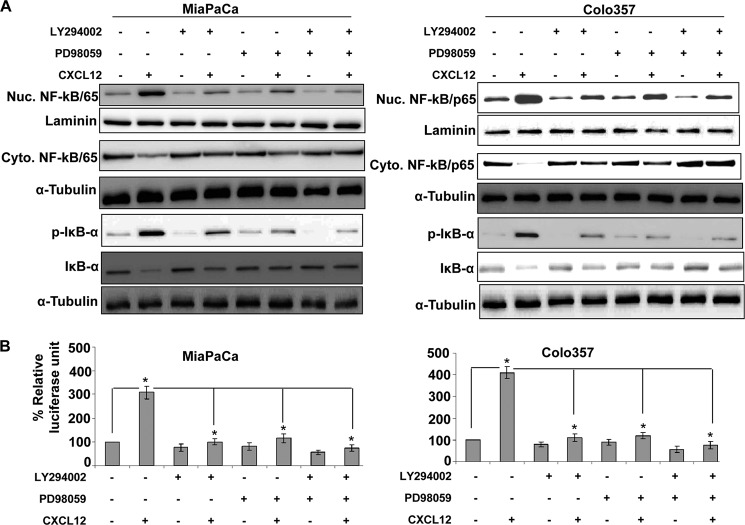
FIGURE 4.
CXCL12-induced activation of Akt and ERK promotes nuclear accumulation and transcriptional activity of NF-κB in pancreatic cancer cells. A, pancreatic cancer cells were pretreated with Akt inhibitor (LY294002, 20 μm) or ERK inhibitor (PD98059, 25 μm) for 1 h, followed by treatment with CXCL12 (100 ng/ml). Total, nuclear (Nuc), and cytoplasmic (Cyto) extracts were prepared after 8 h of CXCL12 treatment to examine effects on NF-κB/p65, p-IκB-α, and IκB-α. Effects on various proteins were examined by immunoblot analysis. Laminin (for nuclear fraction) and α-tubulin (for cytoplasmic fraction) were used as loading controls. B, cells were transiently cotransfected with NF-κB-responsive or control reporter plasmids for 24 h. Subsequently, cells were pretreated (for 1 h) with Akt and ERK inhibitors and stimulated with CXCL12 for the next 24 h. Firefly and Renilla luciferase activities were examined in the treated cells as a measure of NF-κB transcriptional activity and transfection efficiency, respectively. Data are presented as the normalized luciferase units (firefly/Renilla luciferase). Error bars represent the mean of triplicates ± S.D. *, p ≤ 0.01.