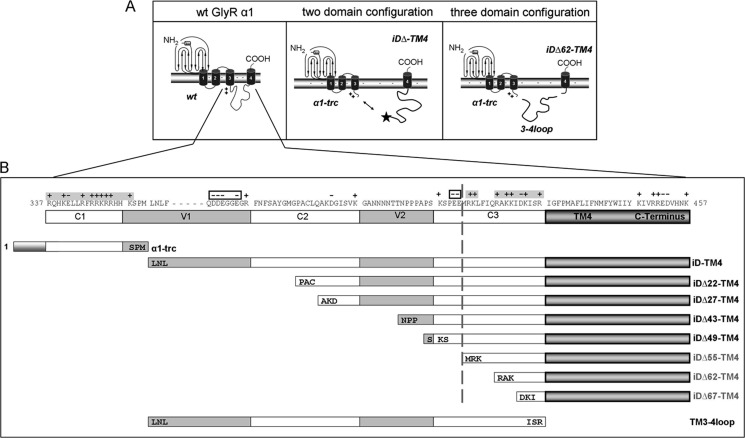
FIGURE 2.
Glycine receptor α1 complementation constructs. A, schematic representation of a single GlyRα1 wild type (wt) subunit (left) the two-domain configuration (middle), and the functional three-domain complementation (right). The localization of the Myc epitope for detection of the construct is marked by a star (middle). Each GlyR subunit consists of a long extracellular N terminus, four transmembrane domains connected by intracellular (TM1-2 and TM3-4) or extracellular (TM2-3) loop structures, and a short extracellular C terminus. The sequence of the long intracellular TM3-4 loop begins with a basic motif, RRKRR, marked by ++. Middle panel, the α1-trc domain includes an artificial stop codon at position 356 (which ends with residues SPM; see B). The iD-TM4 domain consists of the remaining part of the cytoplasmic TM3-4 loop, the TM4, and the C terminus. The right panel shows the three-domain configuration with α1-trc, a truncated complementation construct lacking 62 residues at its N terminus iDΔ62-TM4, and the TM3-4 loop (TM3-4 loop(357–418), representing the lacking 62 residues). B, truncated variants, Myc-iDΔx-TM4, lack amino acids at the construct's N terminus. The numbering is relative to the first amino acid of the immature polypeptide. The TM3-4 loop was subdivided into constant (C1–C3) and variable (V1 and V2) regions. Positive (+) as well as negative (−) residue charge is indicated above the sequence. The α1-trc and all complementation constructs are depicted by bars according to their size, with the first three amino acids of the appropriate construct included (e.g. iD22-TM4 starts with the amino acid residues PAC at the N-terminal end). The TM3-4 loop (TM3-4 loop(357–418)) begins with 357LNL and ends with residues ISR418).