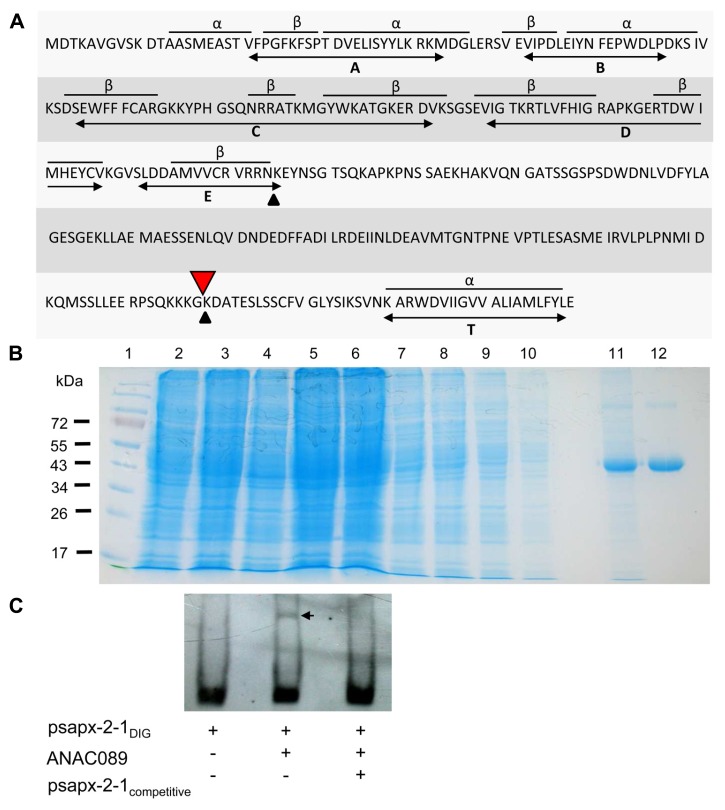
FIGURE 3.
Structure of ANAC089, generation of recombinant His 6-ANAC089 and EMSA. (A) Primary structure of the ANAC089 transcription factor. The N-terminal ANAC domain consists of three α-helices and eight β-sheets in conserved arrangement (A–E). The bioinformatically predicted transmembrane α-helix (T) of the ANAC089 protein is localized at amino acid position 319–339. Putative protein cleavage sites are indicated with arrows. His6-ANAC089 was expressed in E. coli and purified by Ni-NTA affinity chromatography. (B) Heterologous expression and purification of His6-tagged ANAC089. The recombinant ANAC089 protein was expressed in BL21 (DE3) pLysS E. coli cells which were induced with 400 µM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside for 4 h. By SDS PAGE the time-dependent expression of the recombinant ANAC089 protein, as well as the purification process was analyzed. (1) Prestained protein ladder (Fermentas); (2) 0 h after IPTG induction; (3) 2 h after IPTG induction; (4) 4 h after IPTG induction; (5) cell extract; (6) cell pellet; (7–10) column wash fractions; (11) first fraction of ANAC089 elution; and (12) second fraction of ANAC089 elution. (C) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay: ANAC089 promoter fragment interaction in vitro using the DIG Gel Shift Kit (2nd generation, Roche). Verification of the specificity of ANAC089 binding to the cis-element within the sAPX promoter fragment 2-1. Promoter fragment psapx2-1 was loaded at 8 ng DNA. The amount of unlabeled competitor was 2 µg DNA. ANAC089 protein was added at 100 ng. The arrow head marks the shifted band.