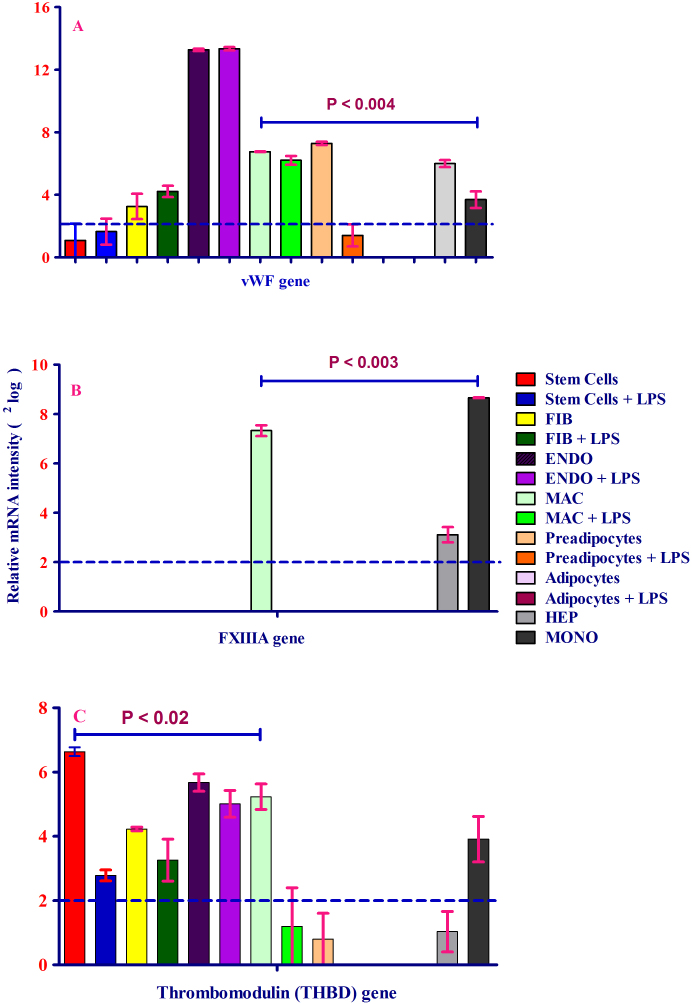
Figure 3. (A-C). mRNA expression of vWF, FXIIIA and thrombomodulin in eight human primary cell types treated either with or without LPS.
The level of each mRNA was measured in triplicate and error bars show standard deviations of means for triplicate cultures per condition and is represented as the mean ± SEM. The p-value obtained from a paired t-test with a two-tailed test samples (T-test). P < 0.05 is considered statistically significant. (A) mRNA expression of vWF in eight different human primary cell types treated with or without LPS. vWF mRNA expression is expressed as 2log values on the y-axis. vWF mRNA expression was detected in all cells tested, except preadipocytes and adipocytes. The highest level of expression was in endothelial cells. Relative mRNA intensity was obtained from three measurements. Hepatocytes served as a positive control for coagulation factor expression. (B) mRNA expression of FXIIIA in eight human primary cell types treated with or without LPS. FXIIIA mRNA expression was synthesized only by macrophages and monocytes. LPS inhibited mRNA expression in macrophages. FXIIIA mRNA expression is expressed as 2log values on the y-axis. Relative mRNA intensity was obtained from three measurements. Hepatocytes served as a positive control for coagulation factor expression. (C) mRNA expression of thrombomodulin (TM) in eight different human primary cells treated with or without LPS. TM mRNA expression was observed in all cells except hepatocytes, preadipocytes and adipocytes (2log lower than or close to 1). TM mRNA expression was inhibited by LPS. TM mRNA expression is expressed as 2log values on the y-axis. Hepatocytes served as a positive control for coagulation factor expression.