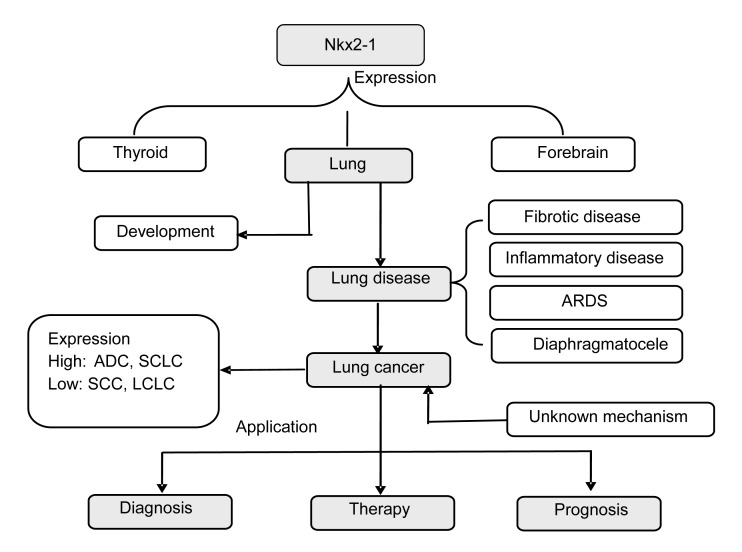
Fig. 2.
A schematic diagram to summarize the role of Nkx2-1 in the lung
Nkx2-1 activates the expression of selected genes in the thyroid, lung, and ventral forebrain, which have a close relationship with the development of the fetal and postnatal lung. Nkx2-1 mutations can induce idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), pulmonary infection, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and diaphragmatic hernia, among other disease processes. Nkx2-1 is highly expressed in lung cancer, especially in ADC and SCLC, while lower expression is found in SCC and LCLC. Nkx2-1 is clinically applicable for lung cancer diagnosis, and as an indicator for therapy type and of prognosis. Understanding the role of Nkx2-1 in lung cancer may open new avenues of research to improve the evaluation of the survival of the lung cancer patients and to develop novel effective therapeutic strategies