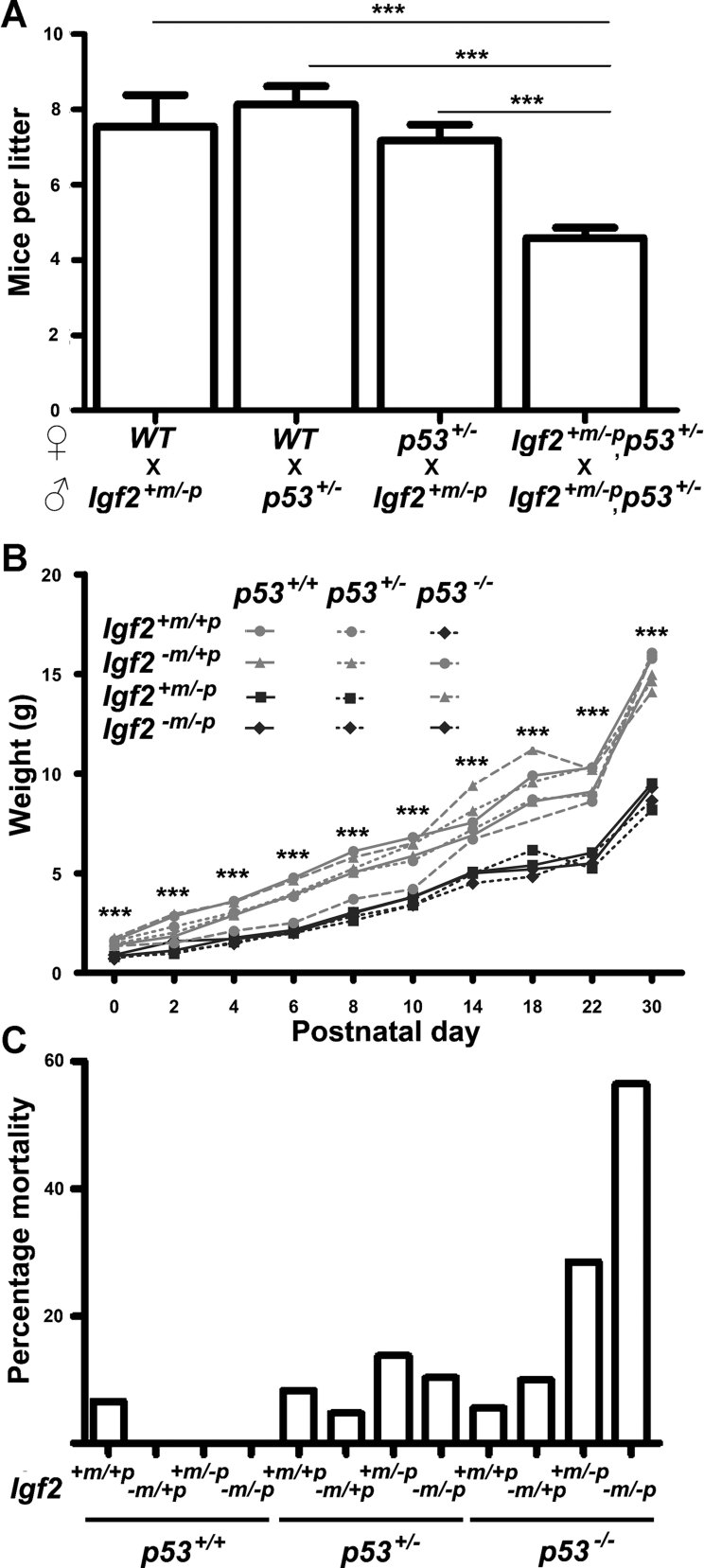
Mean litter size at P0 was significantly reduced from Igf2+m/−p, p53+/− inter-cross (***p < 0.0001, n = 67 litters) relative to Igf2+m/−p mated with WT (n = 11 litters), p53+/− mated with WT (n = 15 litters) and Igf2+m/−p mated with p53+/− (n = 36 litters; one-way ANOVA, Tukey's multiple comparison).
Post-natal growth of progeny from a double heterozygote inter-cross (129, Igf2+m/−p, p53+/−). Mean weights of WT and Igf2−m/+p mice were significantly greater (***p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA, Tukey's multiple comparison) than Igf2+m/−p and Igf2−m/−p mice regardless of allelic dosage of p53.
Increased post-natal mortality by p30 in progeny null for both Igf2 and p53 (Igf2+m/−p, p53−/−, 2 of 7 and Igf2−m/−p, p53−/−, 5 of 9) relative to WT mice (1 of 15, p = 0.037, Fisher's exact test).