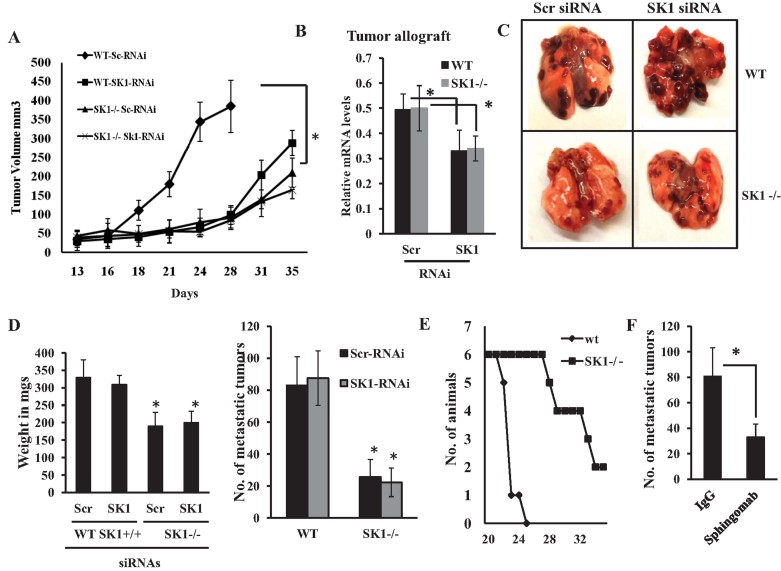
A. Effects of siRNA-mediated SK1 knockdown on MB49-derived allograft tumour growth in the flanks of WT versus SK1−/− mice compared to non-targeting Scr siRNA-transfected controls were measured for 35 days (n = 6/group). Data are represented as mean ± SD. Error bars represent standard deviations. p < 0.05 (*) was considered significant.
B. Efficacy of SK1 knockdown in response to siRNAs in MB49-derived allografts was measured by RT-PCR after surgical removal of tumours from the flanks of WT and SK1−/− mice. Data are represented as mean ± SD. Error bars represent standard deviations. p < 0.05 (*) was considered significant.
C,D. Effects of siRNA-mediated knockdown of SK1 in MB49 cells on lung colonization/metastasis (C) and lung weight or metastatic lung tumour nodules (D, left and right panels, respectively) were measured after tail vein injections for 19–21 days (n = 8/group). Data are represented as mean ± SD. Error bars represent standard deviations. p < 0.05 (*) was considered significant.
E. Effects of the genetic loss of systemic SK1 on overall survival of WT and SK1−/− mice after tail vein injections of MB49 cells were measured for 35 days (n = 8/group).
F. Effects of the pharmacologic inhibition of systemic S1P signalling using Sphingomab on lung colonization/metastasis of MB49 cells were measured for 16 days after tail vein injections compared to controls (n = 8/group). Data are represented as mean ± SD. Error bars represent standard deviations. p < 0.05 (*) was considered significant.