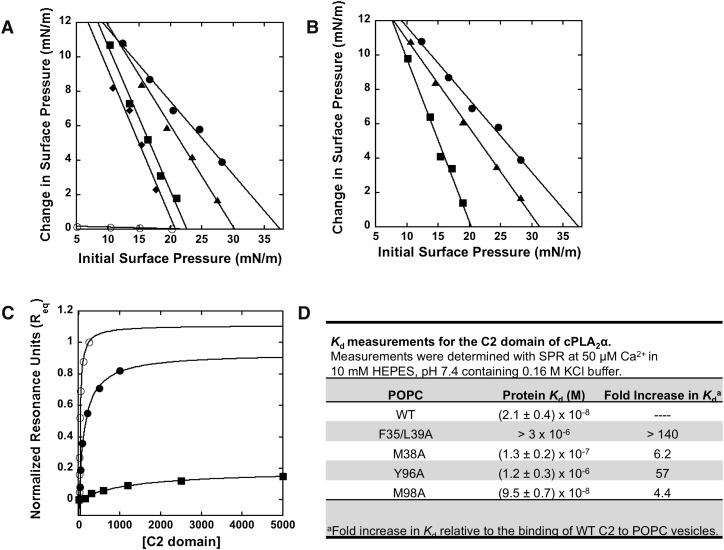
Fig. 5.
Mutations that reduce or abrogate membrane deformation reduce or abolish membrane penetration and membrane affinity. A: Insertion of the wild-type C2 domain in the presence of Ca2+ (filled circles) or EGTA (open circles) into a POPC monolayer monitored as a function of π0. Insertion of F35A/L39A (filled squares), M38A (filled triangles), or D43N (filled diamonds) was also monitored in the presence of Ca2+. B: Insertion of the wild-type C2 domain (filled circles), Y96A (filled squares), or M98A (filled triangles). All measurements were performed in the presence of Ca2+. C: The normalized saturation response (Req) from WT cPLA2α-C2 (filled circles), M38A (filled circles), or Y96A (filled squares) binding at each respective protein concentration was plotted versus C2 to fit with a nonlinear least squares analysis of the binding isotherm [Req = Rmax/(1 + Kd/C)] to determine the Kd. D: Kd values for WT and respective mutations binding to POPC vesicles. The binding experiments were completed from independent experiments in triplicate and are listed with their respective Kd ± SD.