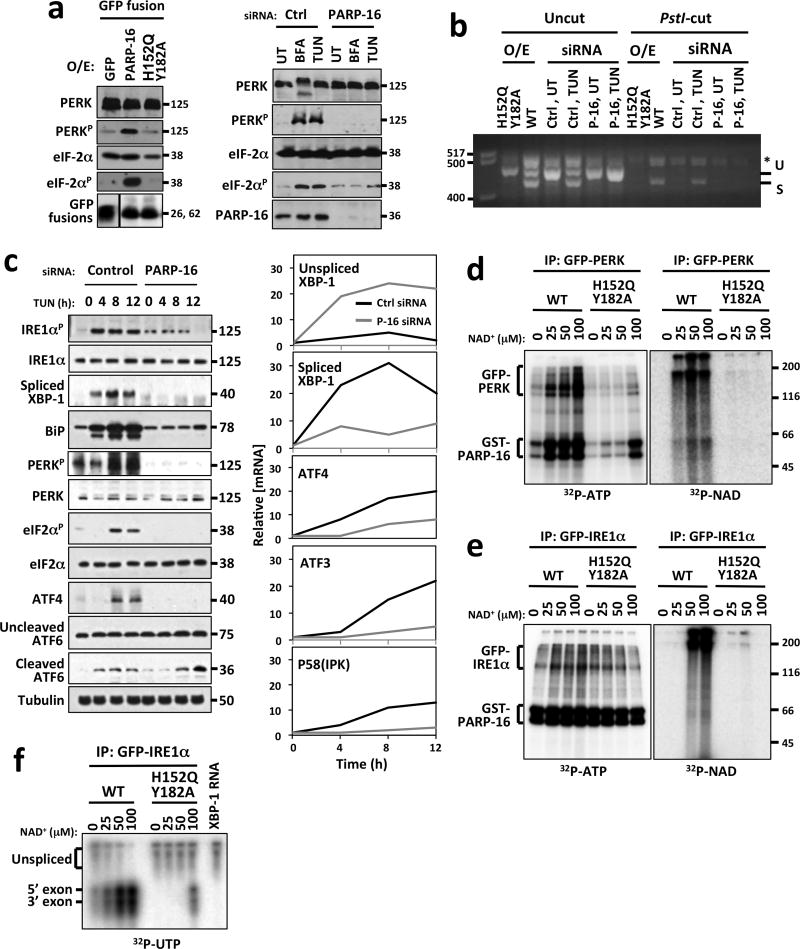
Figure 4. Enzymatic activity of PARP16 is required for activation of PERK- and IRE1α–mediated UPR.
MW (kD or bp) at right or left of blots or gels. (UT)= untreated; (BFA)= Brefeldin A; (TG)= Thapsagargin; (TUN)= Tunicamycin; PERKp= phospho-PERK; eIF2αp= phospho-eIF2 α. Asterisk= hybrid amplicons. a, Left, Immunoblots of cells overexpressing GFP or GFP fusions to PARP16 or PARP16H152Q/Y182A. Right, Immunoblots of cells transfected with control or PARP16 siRNA. b, XBP-1 mRNA splicing assay from control, GFP-PARP16 or GFP-PARP16H152Q Y182A expressing cells, or cells transfected with control or PARP16 siRNA. Unspliced (U) and spliced (S) XBP-1 cDNA were amplified via RT-PCR then cut with Pst1 restriction enzyme. Only unspliced XBP-1 is cut by PstI. c, Left, Immunoblots of cell lysates. Right, RT-qPCR analysis of UPR-dependent transcription in control or PARP16 knock-downs treated with Tunicamycin. d and e, ER microsome based (ADP-ribosyl)ation and kinase assays. Microsomes containing GFP-PERK (d) or GFP-IRE1α (e) were (ADP-ribosyl)ated via addition of 0.5 μg GST-PARP16 or GST-PARP16H152Q Y182A in the presence of 32P-NAD+. Duplicate NAD+ incorporation reactions performed under identical conditions using unlabeled NAD+, then kinase activity assayed via γ32P-ATP incorporation. For d and e, n=4. f, ER microsome based (ADP-ribosyl)ation and IRE1α endonuclease assays. (ADP-ribosyl)ation of GFP-IRE1α was performed in a similar manner to (d) using unlabeled NAD+. In vitro transcribed 32P labeled XBP-1 transcript was incubated with the (ADP-ribosyl)ated GFP-IRE1α immunoprecipitates and assayed for splicing as indicated via presence of 5′ and 3′ exons. n=4.