Figure 2.
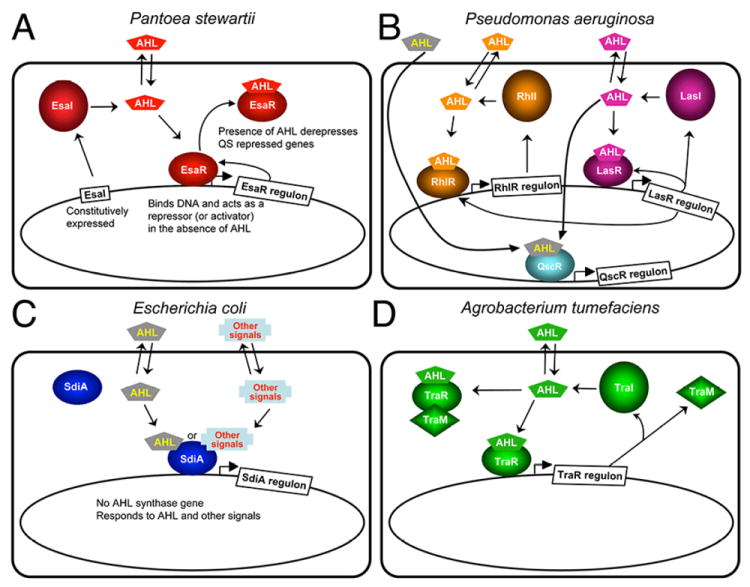
Quorum-sensing systems for which there is structural information. (A) Pantoea stewartii. EsaI constitutively produces 3-oxo-C6-HSL. EsaR binds to the AHL and is derepressed by this binding, which leads to expression of quorum sensing regulated genes in the EsaR regulon and a feedback loop regulating EsaR expression. (B) Pseudomonas aeruginosa. LasI and RhlI produce 3-oxo-C12-HSL and C4-HSL, respectively. The AHLs bind to the cognate R proteins LasR and RhlR, respectively, and activate or repress transcription of the genes in the Rhl and Las regulons. In addition, there is an orphan receptor QscR that has a regulon that overlaps with LasR. QscR can bind to AHLs made by LasI as well as exogenous AHLs that Pseudomonas does not make. The Las system is as at the top of the hierarchy and several feedback loops are found in this quorum sensing system. (C) Escherichia coli. E. coli does not have an AHL synthase, but it does have a LuxR homolog SdiA, which can bind to AHLs and regulate gene expression in response to exogenous AHLs. (D) Agrobacterium tumefaciens. TraI synthesizes 3-oxo-C8-HSL, which binds to TraR, leading to activation of TraR-controlled genes.
