Figure 5.
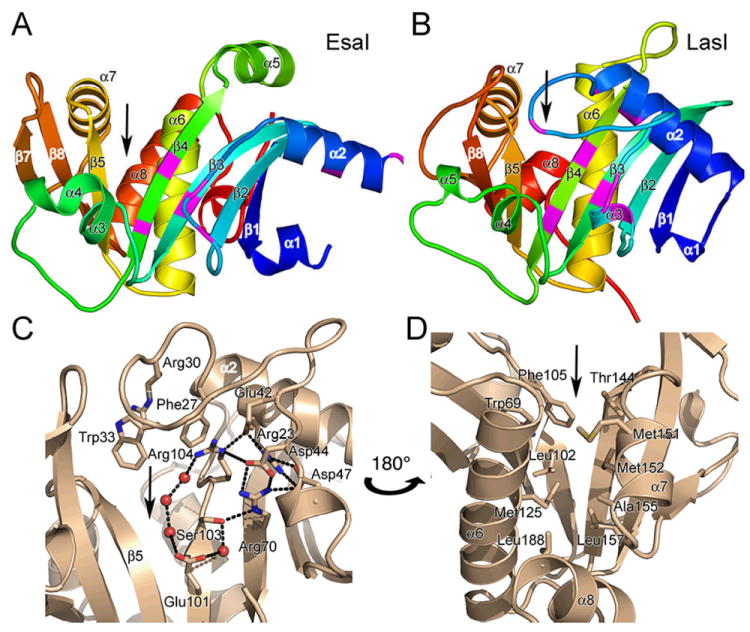
Structure of the AHL synthases EsaI and LasI. (A) Ribbon diagrams depict the backbone structures of EsaI (A) and LasI (B). The structure of the EsaI enzyme (PDB ID 1kzf) from Pantoea stewartii was determined from the native sequence. The structure of the LasI enzyme (PDB ID 1ro5) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa was determined from an active form that had been engineered to improve solubility and crystallization properties. The rainbow coloring is blue to red from the N-terminus to the C-terminus and the major secondary structure elements are labeled. The most conserved residues are indicated with magenta coloring. (C) Close-up view of the LasI active site residues, showing the conserved residues and the electrostatic cluster. Well-ordered water molecules in the active site are shown as red spheres and putative hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted black lines. (D) Close-up view of the LasI acyl-chain binding pocket. The view is rotated approximately 180° about the vertical axis of the page relative to (C) and shows the residues lining the putative acyl-chain binding pocket. In each panel, the active site V-shaped cleft is indicated with a black arrow.
