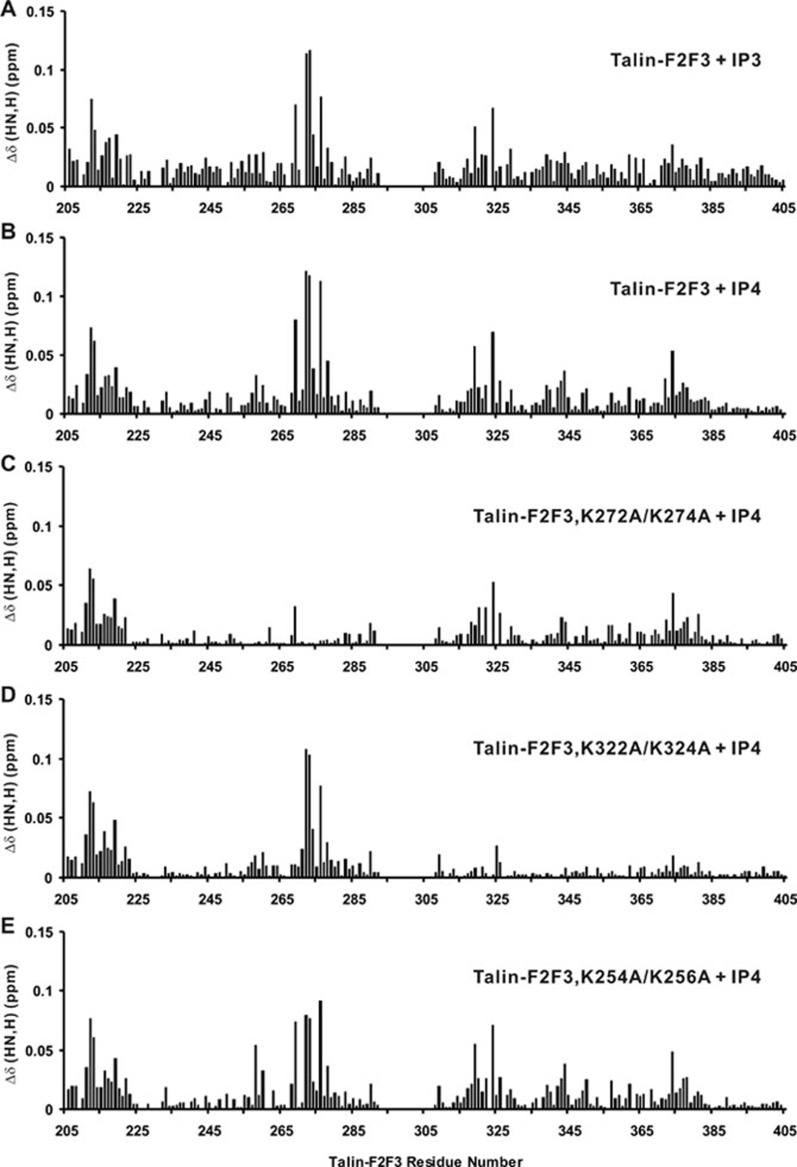
Figure 3.
Mapping of PIP2 and PIP3-binding sites on talin-F2F3 using the corresponding head groups IP3 and IP4, respectively. 1H/15N chemical shift changes of 0.04 mM talin-F2F3 in the presence of (A) 0.8 mM IP3 or (B) 0.2 mM IP4. Both ligands reveal two major similarly perturbed regions with IP4 having a stronger effect likely due to additional negatively charged phosphate group. (C-E) Perturbation profiles of 0.04 mM K272A/K274A (C), 0.04 mM K322A/K324A (D), and 0.04 mM K254A/K256A (E) talin-F2F3 in the presence of 0.2 mM IP4. We note that the N-terminal region of talin-F2F3 is also somewhat perturbed, which is insensitive to these mutations and thus the perturbation is probably due to some secondary effect.