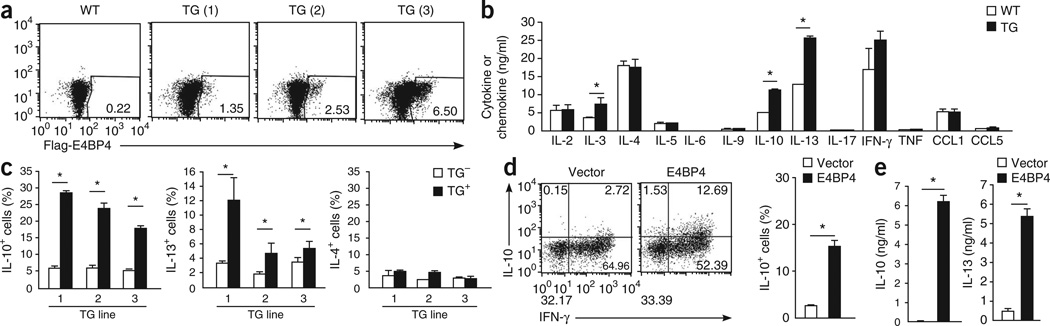
Figure 3.
E4bp4 overexpression induces the expression of IL-10 and IL-13 by CD4+ T cells. (a) Intracellular staining to detect transgene expression by CD4+ T cells purified from the spleens of a wild-type mouse or C57BL/6 mice expressing a transgene (TG) encoding Flag-tagged E4BP4 (three independent lines, TG (1)–TG (3)), assessed with anti-Flag. (b) Concentration of cytokines and chemokines in wild-type and E4bp4-transgenic CD4+ T cells stimulated for 7 d with mAb to TCRβ and mAb to CD28, then restimulated with mAb to TCRβ. *P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test). (c) Intracellular staining to detect T cells producing IL-4, IL-10 and IL-13 among Flag-positive cells (TG+) or Flag-negative cells (TG−) generated from E4bp4-transgenic CD4+ T cells stimulated for 7 d as in b, then restimulated with mAb to TCRβ. *P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test). (d) Intracellular staining to detect T cells producing IL-10 and IFN-γ (left) among GFP+ T cells generated from C57BL/6 CD4+ T cells transduced with plasmid encoding GFP alone or GFP plus E4BP4 and activated under TH1 conditions; right, frequency of IL-10+ cells. (e) Production of IL-10 and IL-13 in the GFP+ T cells isolated in d. *P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). Data are representative of two experiments (a) or are from three independent experiments (b–d; mean and s.e.m.).