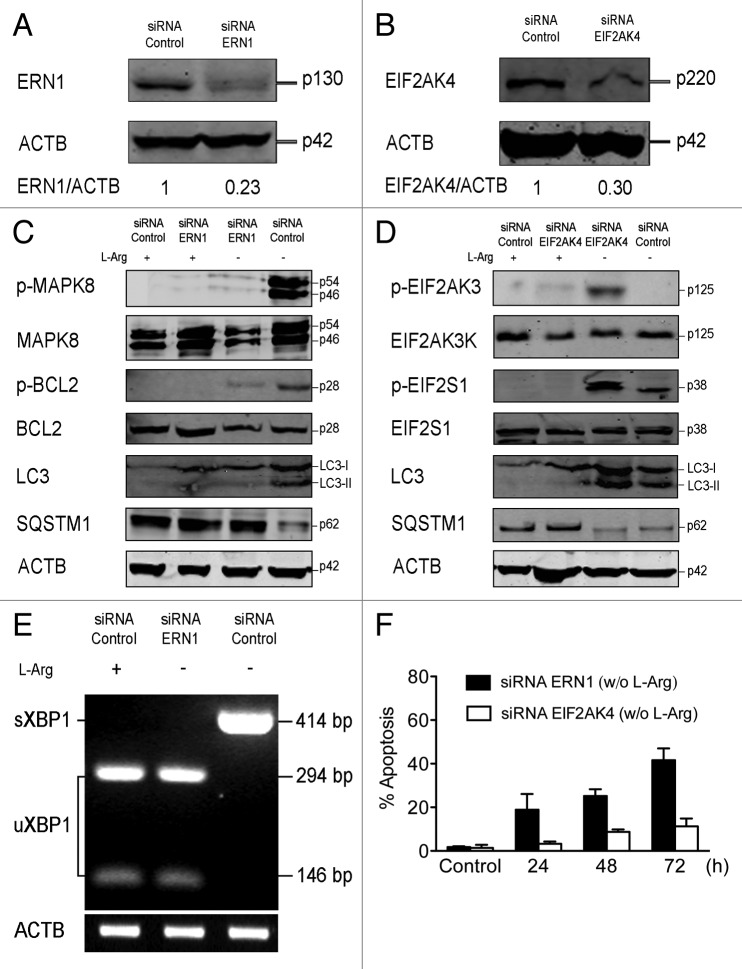
Figure 9. Downregulation of ERN1, but not EIF2AK4, leads apoptosis and inhibition of autophagic flux in Jurkat cells upon L-Arg depletion. (A) Jurkat cells were transiently transfected with 50 nM either control siRNA or siRNA specific to ERN1, and then analyzed by immunoblotting for ERN1 expression. (B) Jurkat cells were transiently transfected with 50 nM either control siRNA or siRNA specific to EIF2AK4, and then analyzed by immunoblotting for EIF2AK4 expression. (C and D) Cells transiently transfected with control siRNA, siRNAs specific to ERN1 (C) or EIF2AK4 (D) were incubated with or without L-Arg for 24 h, and then analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies directed against the indicated proteins. ACTB was used as a loading control. (E) Cells transiently transfected with control siRNA or siRNA specific to ERN1 were incubated with or without L-Arg for 24 h, and then total RNA was isolated and subjected to semiquantitative RT-PCR using specific primers for the XBP1 gene. PCR amplicons were incubated with PstI, and then run in agarose gel electrophoresis and stained with ethidium bromide. Only cDNA derived from sXBP1 mRNA was not cut with PstI, because of the loss of a 26-bp intron in response to ER stress. The positions of the amplification products uXBP1 and sXBP1 are indicated. Expression of ACTB was used as a loading control. (F) At 24 h after transfection, cells transiently transfected with siRNA to ERN1 and siRNA to EIF2AK4 were incubated in medium without L-Arg for 24, 48 and 72 h. At the indicated times cells were stained with FITC-annexin V and 7-ADD. Annexin V-positive populations were determined by flow cytometry, and represented the percentage of apoptosis. Data shown are means ± SD or representative experiments of three performed.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.