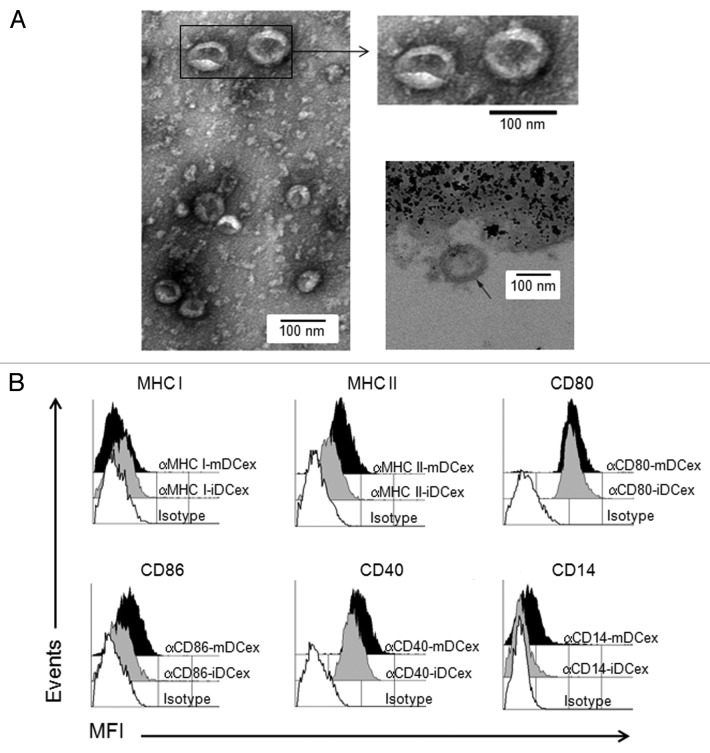
Figure 1. Purified DCex have oval-biconcave shape, 30 to 100 nm in diameter and DC phenotype. iDC and mDC were generated by culturing linage marker-negative bone marrow cells in the presence of GM-CSF/IL4 and GM-CSF/IL4/LPS, respectively. DCex were isolated from conditioned media of these DC cultures using fractionated centrifugation and filtrations. Morphology (A) and surface markers (B) of purified DCex were examined by TEM and flow cytometry, respectively. (A) Purified iDCex either unbound or bound to anti-Class II MHC antibody-coated beads were processed for and examined using TEM. The left and the upper right panels of TEM micrographs of purified DCex show several 30–100 nm diameter oval-biconcave structures. The lower right panel is a TEM micrograph of a DCex bound to anti-Class II MHC antibody-coated beads showing a section of an oval structure having an electron-dense double layer membrane structure that surrounds an electron-clear material (indicated with the arrow), attached to amorphous bead structure. (B) Purified iDCex and mDCex were captured onto anti-Class II MHC antibody-coated beads, stained with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies specific for the DC markers Class I MHC (αMHC I), Class II MHC (αMHC II), CD80 (αCD80), CD86 (αCD86), CD40 (αCD40) and CD14 (αCD14), as well as isotype control antibodies (Isotype), and analyzed by flow cytometry. Data are mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of a representative experiment of 4 independent experiments performed.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.