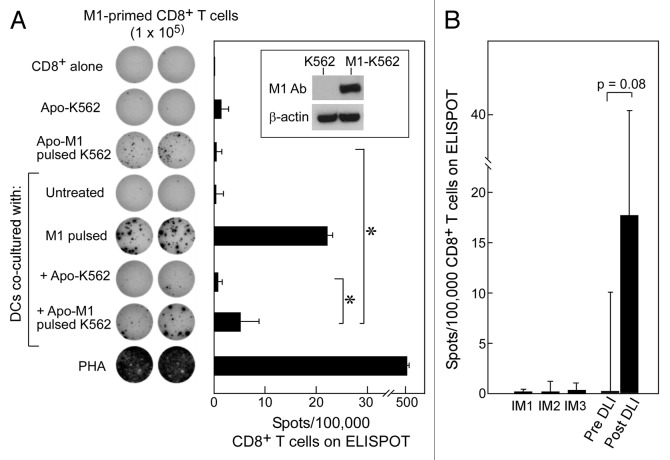
Figure 4. Apoptotic K562 cells when presented on DCs can stimulate antigen-specific immunity against either introduced or native antigen. (A) K562 cells were transfected to express M1 (see inset) and then irradiated with 400 mJ UVB to induce apoptosis. Following irradiation, these cells were co-cultured with iDCs for 24 h and matured using a cytokine cocktail for 24 h. On ELISpot, we used CD8+ T cells alone as a negative control, M1-pulsed DCs and PHA as positive controls, and apoptotic M1-K562 and DCs alone on CD8+ T-cells to establish background reactivity. There was a significant increase in reactivity of apoptotic M1-K562 when cross-presented by DCs compared with apoptotic M1-K562 cells alone (*p = 0.04) or DC cross-presented apoptotic K562 cells (p = 0.04). Significance was determined using the two-tailed Student’s t test. All experiments were performed in duplicate wells, and mean spot-forming cells per 100,000 CD8+ T cells are reported. Error bars represent two standard deviations. The ELISpot image is representative of more than 3 experiments, while the bar graph displays average results from four experiments, with standard deviation as shown. (B) T cells from pre- and post-DLI patients were tested on ELISpot against CML antigens in the form of apoptotic K562 cross-presented on DCs, and results were reported as spots per 100,000 CD8+ T cells (minus background, defined as reactivity of apoptotic K562 cells alone or autologous DCs alone on CD8+ T cells); p = 0.08 (Student’s t test). Three patients treated with imatinib were tested as comparison, and showed no reactivity. Results are shown as means with error bars representing two standard deviations.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.