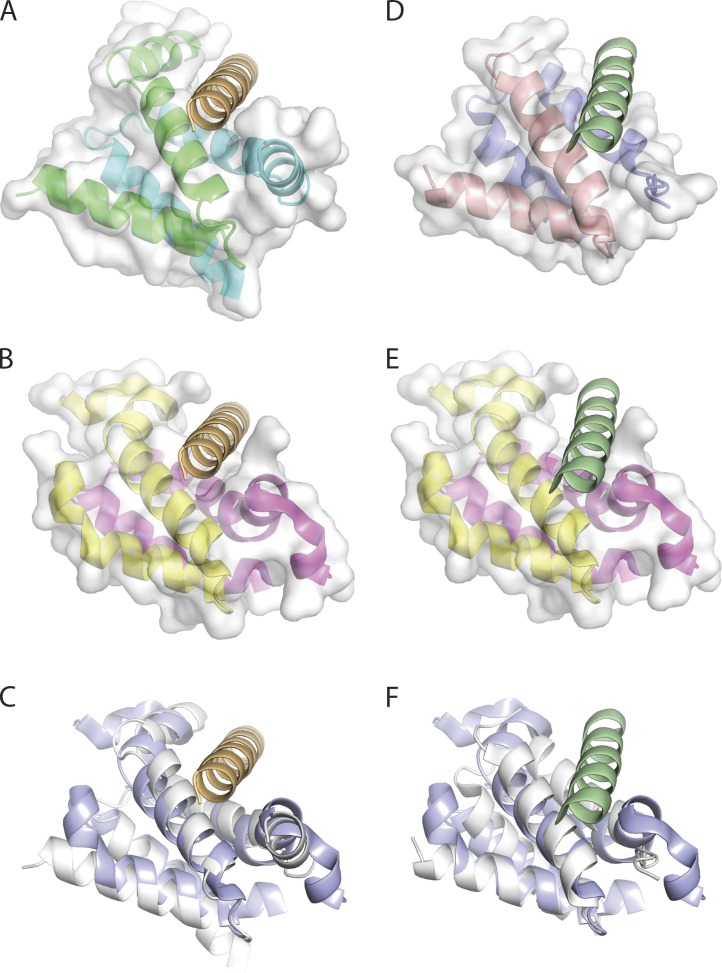
Figure 9.
Similarity in x-ray structures of RIIa and Dpy-30 D/D domains with bound and superposed AHR peptide. (A) The PKA regulatory subunit RI D/D domain dimer in complex with the dual-specific D-AKAP2 AH (PDB accession number 3IM4 [Sarma et al., 2010]). The RI D/D dimer is represented in cartoon format and is colored by chain (cyan and green). The van der Waals surface for the RI D/D dimer is in semi-transparent white and the complexed D-AKAP2 AHR is in orange. (B) The human Dpy-30 C-terminal domain (PDB accession number 3G36 [Wang et al., 2009]) represented in cartoon format and colored by chain (pink and yellow). A structural overlay with the RI/D-AKAP2 structure (C) reveals that the dual-specificity AKAP2 AHR peptide can be accommodated in the Dpy-30 docking site. (C) Structural overlay of the D/D domains of human Dpy-30 (PDB accession number 3G36; blue) with the RI (PDB accession number 3IM4; white). The root mean squared deviation for equivalent polypeptide chains is 1.7 Å. (D) The PKA regulatory subunit RII D/D domain dimer in complex with the D-AKAP2 AH (PDB accession number 2HWN [Sarma et al., 2010]). The RII D/D dimer is represented in cartoon format and colored by chain (red and blue). The complexed D-AKAP2 AHR is colored in green. (E) A structural overlay of the human Dpy-30 C-terminal with the RII/D-AKAP2 structure (F) reveals that the dual-specificity AKAP2 AHR peptide can be accommodated in the Dpy-30 docking site. (F) Structural overlay of the D/D domains of human Dpy-30 (PDB accession number 3G36; blue) with the RII (PDB accession number 2HWN; white). The root mean squared deviation for equivalent polypeptide chains is 1.4 Å.