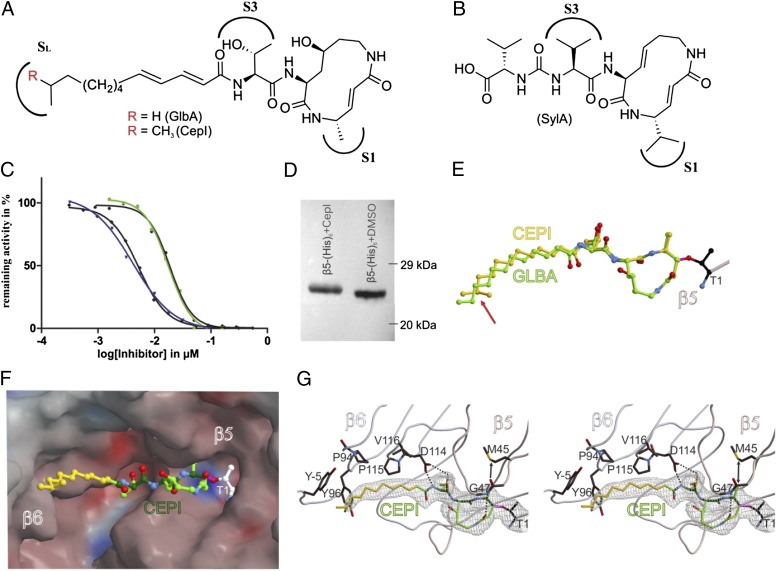
Fig. 2.
In vitro functional and structural characterization of GlbA and CepI. (A) NMR-deduced structures of GlbA/CepI with the proteasome binding sites S1 and S3 as well as the hydrophobic patch SL. (B) SylA, featuring a hydrophilic carboxylic acid tail. (C) IC50 curves for the ChTL activity measured for GlbA (green) and CepI (blue) with 13C-labeled peptide substrate; black curves depict equivalent measurements with the fluorogenic Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC substrate (error bars are too small to be visible). (D) Western blot on a β5-(His)6 yeast CP mutant with or without treatment with CepI. The gel shift indicates an increased molecular mass by covalent and irreversible binding. (E) Structural superposition of GlbA and CepI bound to yeast CP; the differing methyl moiety is indicated by a red arrow. (F) Surface representation of CepI in the β5 substrate binding channel. Colors indicate positive and negative electrostatic potentials contoured from −30 kT/e (bright red) to +30 kT/e (bright blue). (G) Stereoview of the 2Fo − Fc omit electron density map (gray mesh, 1σ) for the β5 active site. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by dashed lines, whereas the arrow pronounces the accurate fitting of the P1 methyl side chain of the inhibitor. The lipophilic pocket of the SL site is formed by Tyr−5, Pro94, Tyr96, and Pro115 from β6 [amino acid numbering according to Löwe et al. (25)].