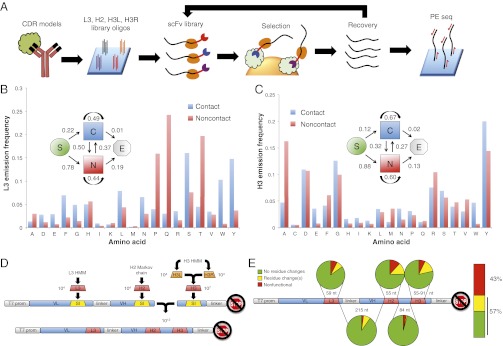
Fig. 1.
HMM antibody library design and synthesis. (A) Strategy for design and application of the rationally designed scFv library. Antigen–antibody crystal structures are used to design CDR-encoding DNA sequences, which are then synthesized on a programmable microarray. After ribosome display and enrichment for antigen binding clones, library recovery, and analysis by paired-end sequencing can be performed. (B) Model-defining parameters for the L3 HMM. Emission probability for each amino acid corresponding to the two possible states. State transition probabilities are inset: “S” denotes start of a chain, “C” denotes the contact state, “N” denotes the noncontact state, “E” denotes the end of the chain. (C) Model-defining parameters for the H3 HMM. Definitions are the same as for B. (D) Overview of the scFv ribosome display vector and library assembly strategy. “VL” and “VH” are the light and heavy variable domains, respectively. “T7 prom” is the T7 promoter, and the crossed stop sign denotes lack of a stop codon. L3, H2, and H3 are the CDR libraries designed to replace the “SI” suicide inserts. H3L and H3R sublibraries are brought together by combinatorial ligation to create H3. Similarly, the L3-H2 fragment is brought together with the H3 fragment in a combinatorial ligation. (E) Clonal Sanger sequencing analysis of 93 HMM scFv library members.