Fig. 4.
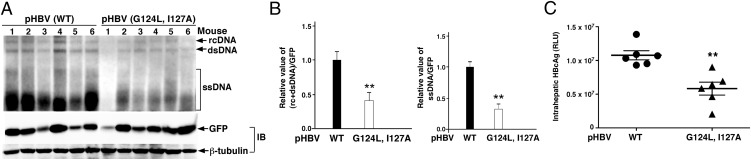
Interaction between HBx and Bcl-2 proteins is critical for HBV DNA replication in mouse hepatocytes. (A) Southern blot analysis of HBV DNA replication in mouse livers after hydrodynamical injection of the wild-type or the mutant (G124L, I127A) pHBV replicon 2 d postinjection. pcDNA3-GFP was coinjected as an injection marker. Equivalent amounts of liver tissues from six BALB/C mice in each injection group were collected and subjected to HBV DNA and HBcAg analyses (Materials and Methods). The levels of GFP and β-tubulin were determined by immunoblotting (IB) and used as controls to normalize the transfection efficiency. (B) Quantification of viral DNA intermediates from the Southern blot analysis in A. The results represent the relative value of different HBV DNA intermediates to the GFP control. The amounts of DNA and GFP were quantified by Quality One software (Bio-Rad). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01. (C) A plot showing the levels of the HBV core protein (HBcAg) in mouse livers. All mice (n = 6) from each injection group were subjected to HBcAg analysis (Materials and Methods). RLU represents relative luminescence units (mean ± SEM). **P < 0.01.