Figure 7.
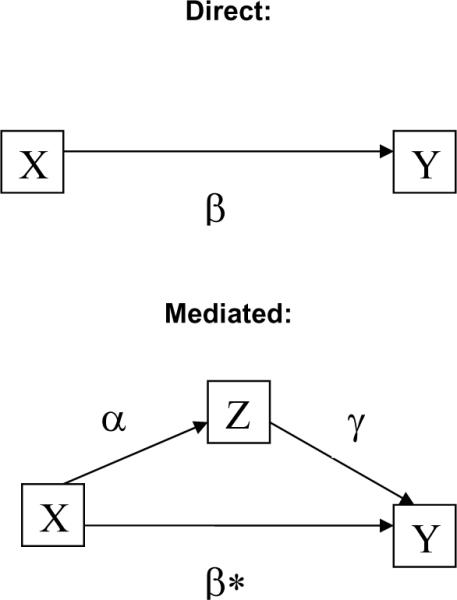
Model of interaction of errors and analyses, direct and mediated. Y is the outcome of interest (e.g., blood pressure), X is the predictor of interest (e.g., drug group in placebo vs. active agent), Z is a known covariate of interest (e.g., gender), and W is a variable collected as part of the study, but not considered in the analysis. Observed correlation between X and Y is defined as: ρXY = ρTU * ρX * ρY, where ρXY is the observed correlation between X and Y, ρTU is the correlation that would have been observed if X and Y had been measured with perfect reliability, and ρX and ρY are the square root of the reliabilities of X and Y, respectively.
