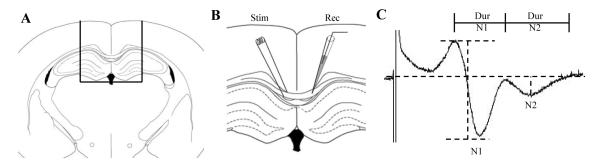
Figure 1.
Measurement of compound action potential (CAP) in the corpus callosum. (A) Representative schematic of the coronal slice containing the corpus callosum used for recording the CAP. (B) Stimulating and recording electrodes were placed approximately 0.5 mm on either side of the midline. (C) Representative trace of a typical CAP used to measure the amplitudes. The amplitude of the N1 component (myelinated fibers) was the difference in voltage from the first positive peak to first negative trough; the amplitude of the N2 component (unmyelinated fibers) was measured by dropping a tangent from the baseline to the second negative trough. The duration of N1 was measured as the time between the first and second positive peaks; the duration of N2 was measured as the time between the second positive peak until the signal returned to baseline.