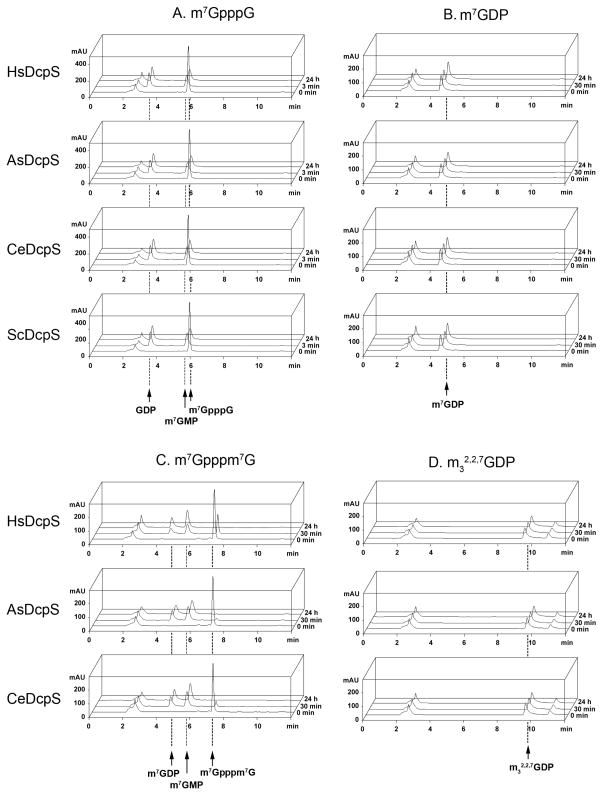
Figure 2.
HPLC analysis of hydrolytic susceptibility of m7GpppG, m7Gpppm7G, 7-methylguanosine diphosphate (m7GDP), and 2,2,7-trimethylguanosine diphosphate (m32,2,7GDP) to recombinant DcpS. All experiments were performed using condition set (2): 20 °C in 50 mM Tris HCl buffer containing 200 mM KCl, 0.5 mM EDTA and 1 mM DTT (final pH 7.6) with 0.2 μM DcpS. Initial concentrations of cap analogs were 15 μM. The HPLC peak with a retention time of 2.5 min corresponds to the reaction buffer.
(A) DcpS enzymes efficiently hydrolyze m7GpppG. Complete conversion of the substrate to m7GMP and GDP products occurs within less than 3 minutes.
(B) and (D) m7GDP and m32,2,7GDP, respectively, are not hydrolyzed following 24 h of incubation with DcpS. The HPLC peak with a retention time of 10.8 min in the m32,2,7GDP profile corresponds to a substrate contaminant.
(C) Hydrolysis of m7Gpppm7G is significantly slower than that of m7GpppG. After 30 min, a small amount of the substrate is still observed in all cases. Chromatographic peaks corresponding to the products, m7GDP and m7GMP, retain their intensity after the complete degradation of m7Gpppm7G (24 h of investigation), confirming the resistance of m7GDP to enzymatic cleavage.