FIG. 7.
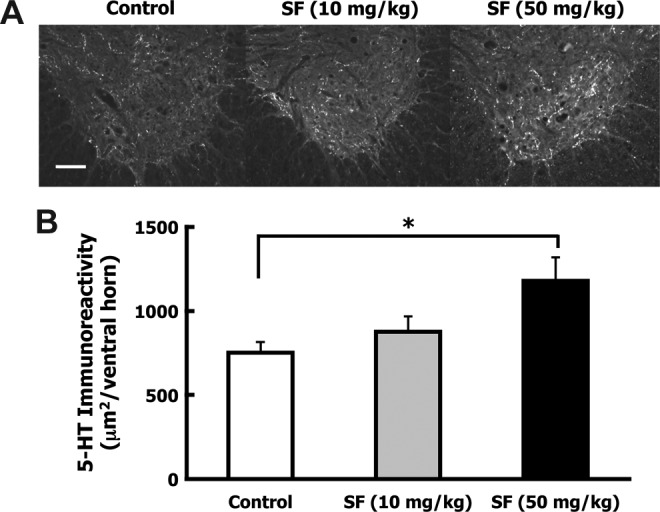
Sulforaphane (SF) treatment increased serotonergic axons caudal to the contusion injury site. After spinal cord injury (SCI), animals received IP injections of corn oil (control; n=7), low-dose SF (10 mg/kg; n=8), or high-dose SF (50 mg/kg; n=7) at 10 min and 72 h following injury. Five weeks after injury the animals were euthanized, perfusion-fixed, and the spinal cords were dissected. Transverse sections ∼7.5 mm caudal to the lesion were immunostained for serotonergic (5-HT) fibers and immunoreactivity was quantified in the ventral horns of five sections. (A) Representative ventral horn 5-HT immunostaining is shown for control, low-dose, and high-dose SF animals (scale bar=100 μm). (B) Bars indicate the average 5-HT pixel density area per ventral horn (mean±standard error of the mean). A significant 57% increase in 5-HT-stained area was detected in the ventral horns of the high-dose SF-treated group over the control group (*p<0.05 by one-way analysis of variance).
