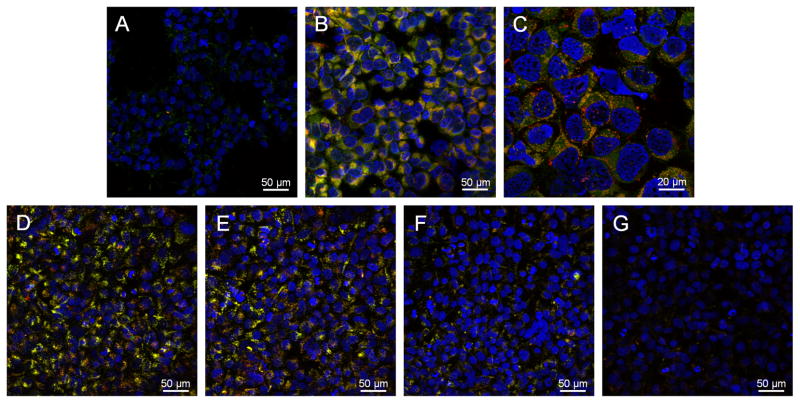
Figure 4.
Fluorescent NPs, labeled at the PEG termini with fluorescein (green) and loaded with the hydrophobic fluorophore ETTP5 (red), exhibit affinity towards scavenger receptor A1, a key mediator of oxLDL accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions. NPs appear yellow in fields supported by stable colocalization of core-shell fluorophores. HEK cells engineered to express SR-A1 were incubated overnight (A–C) or for 6 h (D–E) with fluorescent NP 1, [AM 1] = 10−5 M. Confocal images of NP binding/uptake in basal cells with low SR-A1 expression (A) and following SR-A1 expression (B) indicate substantial NP interaction with SR-A1. C) Higher magnification image of cells with positive SR-A1 expression clearly showing NP association/internalization. Primary SR-A1 mAb (mouse antihuman) or polyinosinic acid (PIA), a well known ligand for SR-A1, blocking experiments (D–G) confirms NP affinity towards SR-A1. D) NPs incubated with SR-A1 expressing cells and following incubation with E) 10 μg mL−1 isotype control antibody (IgG1), F) 10 μg mL−1 primary anti-SR-A1 monoclonal antibody and G) 10 μg mL−1 PIA for 6h. Yellow signal indicates co-localization of both fluorophores associated with the NP. Cell nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342.