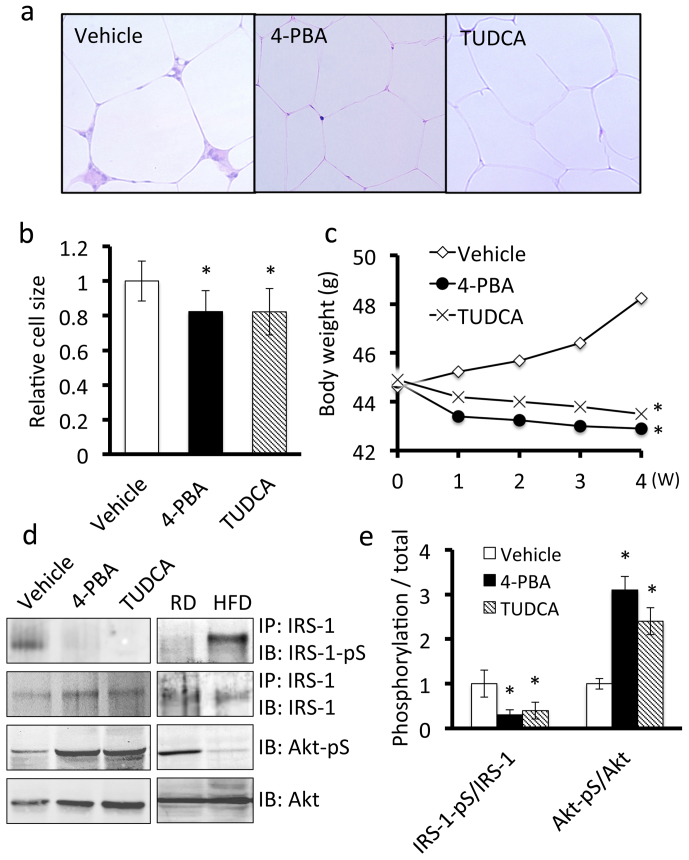
Figure 5. ER stress contributes to symptoms of obesity in adipose tissue of mice fed a high-fat diet.
Mice were fed a high-fat diet for 16 weeks and then treated with 4-PBA or TUDCA for 4 weeks at a dose of 1 g/kg/day. A, H&E staining of adipose tissue. Treatment with 4-PBA or TUDCA inhibited macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue and slightly decreased the size of the adipocytes. B, Quantitative analysis of the size of adipocytes treated with 4-PBA or TUDCA. Values are mean ± SD (n = 5). *p < 0.05 (unpaired Student's t-test). C, Effects of 4-PBA or TUDCA on body weights of mice fed a high-fat diet. The body weights of obese mice treated with 4-PBA (n = 7) or TUDCA (n = 8) were significantly lower than those of vehicle-treated obese mice (n = 8). *p < 0.05 (unpaired Student's t-test). D, Western blot analysis of insulin signaling components in adipose tissue. Adipose tissue lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting. Treatment with 4-PBA or TUDCA down-regulated the expression of phospho-IRS-1 at Ser307 (IRS-1-pS) and up-regulated the expression of phospho-Akt at Ser473 (Akt-pS) (Left panel). Mice were fed regular diet or a high fat diet for 20 weeks (Right panel). E, Quantitative analysis of phospho-IRS-1 and phospho-Akt expression levels in adipose tissue. Values are mean ± SD (n = 5). *p < 0.05 (unpaired Student's t-test).