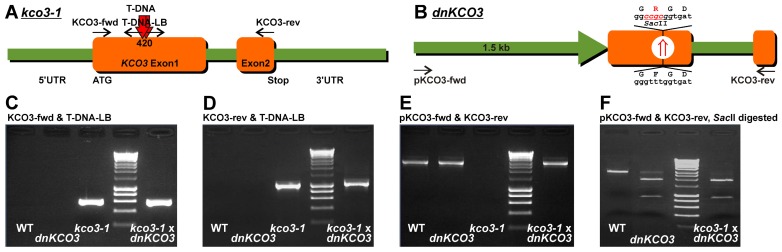
FIGURE 1.
Genotyping of kco3-1 null-allele, dnKCO3 and kco3-1 × dnKCO3 mutant plants. (A) Schematic representation of the Salk_96038 T-DNA insertion line that contains two head to head T-DNA insertions at position 420 in the first exon of the KCO3 gene. (B) Schematic representation of dnKCO3 mutant, where, in the first exon of the KCO3 gene, a dominant negative mutation has been created by mutating the GFGD motif to GRGD. Additionally, a recognition site of the restriction enzyme SacII has been inserted. (C,D) PCR was performed on genomic DNA with the indicated primer sets specific for T-DNA amplification. Amplification was attained in case of kco3-1 and kco3-1 × dnKCO3 while the wild-type and dnKCO3 does not show any amplification product with the T-DNA primer sets. (E) PCR was performed with the indicated gene specific primer pair. Amplification can be observed in Col-0 wild-type, dnKCO3 and kco3-1 × dnKCO3. No amplification product is detectable in the homozygous T-DNA insertion line (kco3-1). (F) SacII restriction digestion of the PCR products obtained by amplification with the gene specific primer pair. PCR product from Col-0 wild-type was not digested. The amplification product from the dnKCO3 mutant was digested but some undigested product can also be seen. The PCR product from kco3-1 × dnKCO3 shows complete digestion.