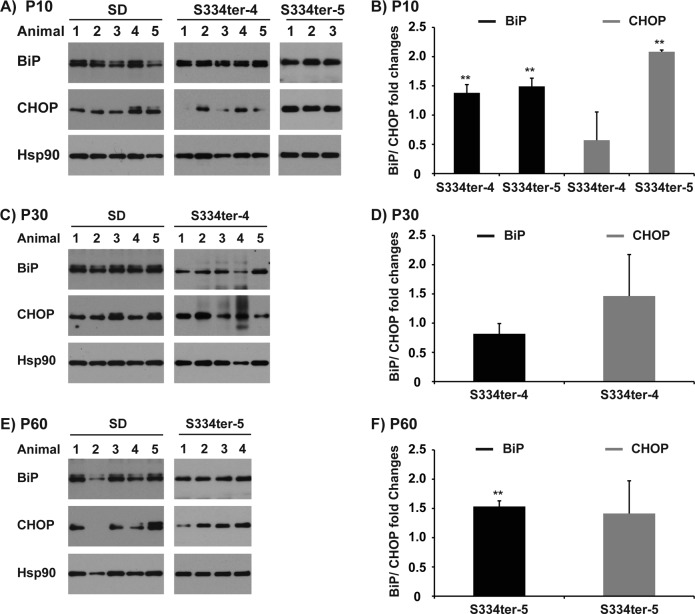
Figure 2. .
Induction of BiP and CHOP protein in retinas of mutant rhodopsin rats. (A) BiP and CHOP protein levels from total retinal protein lysates from three to five Sprague-Dawley, S334ter-4, and S334ter-5 rats at postnatal day 10 (P10) were examined by immunoblotting. Mean value and SD of BiP or CHOP protein levels in S334ter-4 and S334ter-5 cohorts at P10 relative to age-matched Sprague-Dawley controls are plotted in (B). (C) BiP and CHOP protein levels from total retinal protein lysates from five Sprague-Dawley or S334ter-4 at P30 were examined by immunoblotting. Mean value and SD of BiP and CHOP protein levels in S334ter-4 cohorts at P30 relative to Sprague-Dawley controls are plotted in (D). (E) BiP and CHOP protein levels from total retinal protein lysates from four to five Sprague-Dawley or S334ter-5 rats at postnatal day P60 were examined by immunoblotting. Mean value and SD of BiP and CHOP protein levels in S334ter-5 cohorts at P60 relative to Sprague-Dawley controls are plotted in (F). (A, C, E) HSP90 protein levels are shown as loading control. P values represent the following asterisk system: **P < 0.005