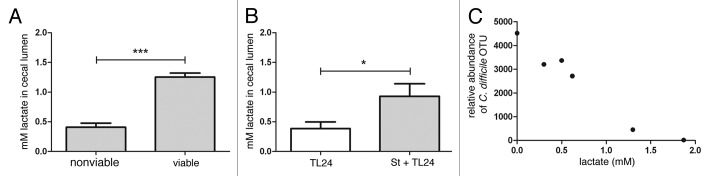
Figure 3.S. thermophilus treatment increases levels of cecal lactate and is correlated with lower levels of C. difficile. (A) Antibiotic treated, uninfected mice receiving subsequent treatment with viable S. thermophilus had significantly higher levels of cecal lactate vs. mice receiving UV-irradiated (nonviable) S. thermophilus (***p = 0.0009; n = 3/group). (B) Mice treated with S. thermophilus before and after C. difficile infection maintained significantly higher cecal lactate levels (*p = 0.04) vs. untreated, infected mice. (C) An inverse correlation between cecal lactate and abundance of C. difficile OTUs from cecal luminal contents were calculated (two-tailed, Spearman r = -0.942, p = 0.017).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.