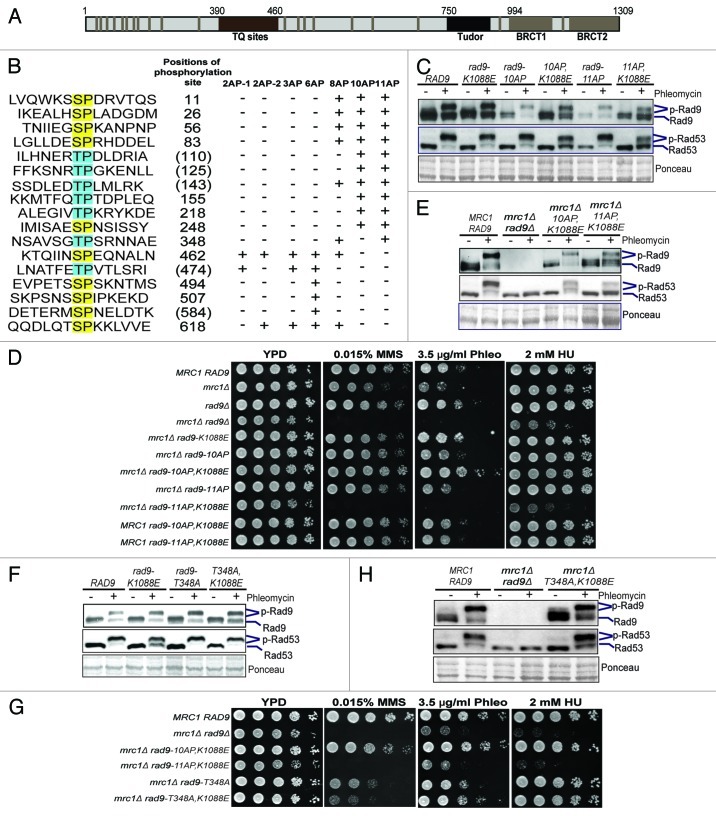
Figure 2. The N-terminal SP/TP sites of Rad9 are involved in DNA damage checkpoint activation. (A) Schematic of Rad9 domain structure and the consensus CDK phosphorylation sites (gray bars). (B) Summary of the Rad9 SP/TP phosphorylation sites, which are mutated as indicated in each rad9-AP mutant. Positions of the Ser/Thr residues are indicated to their right. Parentheses indicate phosphorylation not detected by MS.8 “+” indicates Ser/Thr-to-Ala mutations. “-“ indicates no mutation. Gel mobility shift assays of Rad9-3HA and Rad53 were performed in G2/M-arrested cells as indicated in (C and F). Plate sensitivity assays of MMS, phleomycin (Phleo) and HU with WT, mrc1Δ, rad9 and various double mutants of mrc1Δ rad9 were performed in (D and G). Gel mobility shift assays were performed using asynchronous cells, comparing WT and various double mutants of mrc1Δ rad9 as indicated in (E and H).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.