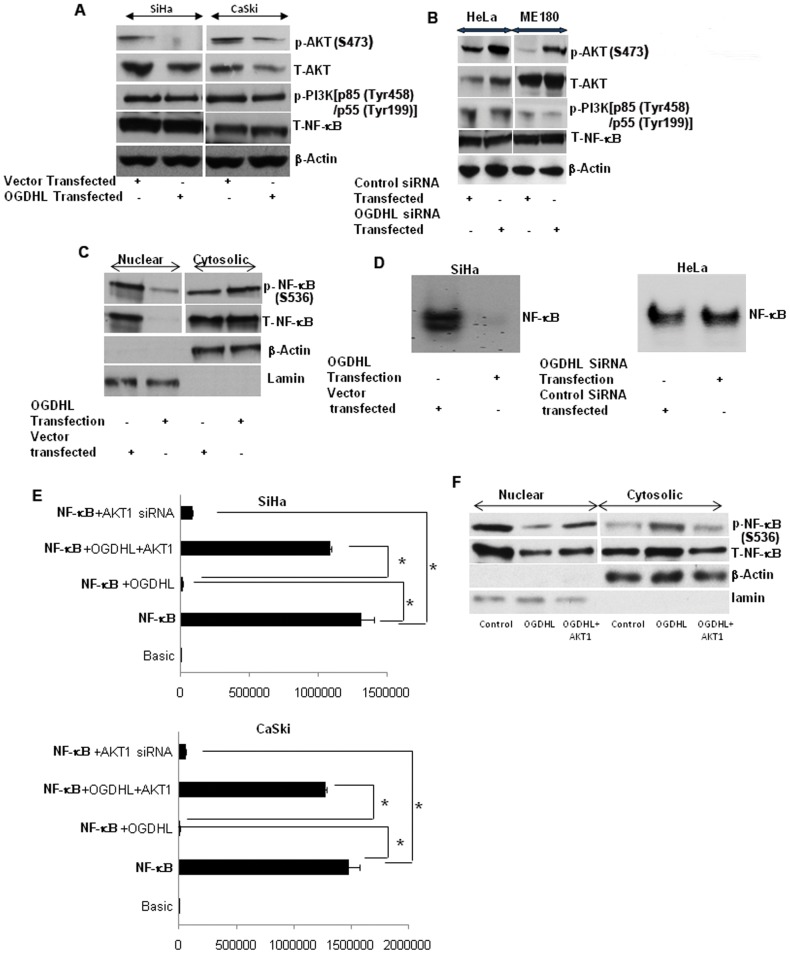
Figure 5. Immunoblotting analysis of phospo-AKT , total-AKT, phospo-PI3K, total- NF-κB and β-actin.
In A. SiHa and CaSki cell lines 48 hours after transient transfection of OGDHL and empty vector; and B. HeLa and ME180 cell lines after OGDHL siRNA and scramble siRNA transfection; OGDHL inhibition by OGDHL siRNA has dramatic effect on total AKT and phospho-AKT level C. Immunoblotting analysis of phospo-NF-κB and total-NF-κB of SiHa cell lines 48 hours after OGDHL and empty vector transfection; β-actin and lamin was used as a loading control for cytosolic and nuclear fraction respectively; NF-κB translocation from cytoplasm towards the nucleus was decreased after OGDHL overexpression in SiHa cells; D. NF-κB gel shift assay in SiHa and HeLa cell lines; OGDHL overexpression in SiHa cells decreased the DNA binding activity of NF-κB compared to that of empty vector control; OGDHL siRNA increase the binding activity of NF-κB in HeLa cell; E. NF-κB luciferase assay in SiHa (upper panel) and CaSki (lower panel) cell lines after transient over-expression of OGDHL with or without AKT1 over-expression. It is evident that OGDHL suppresses AKT activity and lead to inhibition of NF-κB-dependent gene transcription (* p<0.001). F. Immunoblotting analysis of phospho- NF-κB, total- NF-κB, β-actin and lamin in nuclear and cytosolic fractions of SiHa cell lines after OGDHL over-expression with or without AKT1 overexpression. The data showed that co-transfection of OGDHL and AKT1 partially increased the translocation of NF-κB from the cytoplasm to the nucleus.