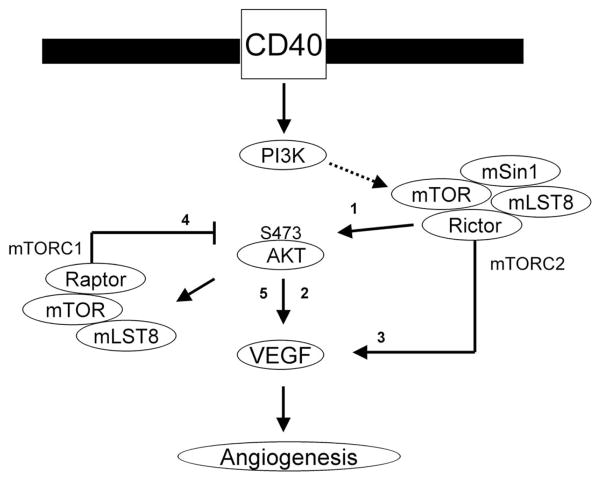
FIGURE 6.
Model illustrating CD40-induced signals that mediate the expression of VEGF in endothelial cells. Our previous report (16) demonstrated that the ligation of CD40 mediates VEGF expression through the Ras and PI3K signaling pathway. In these studies, we found a critical role for mTOR and Rictor (mTORC2) in CD40-induced phosphorylation of Akt (arrow 1), a function for Akt in VEGF expression (arrow 2) and a function for mTORC2 in CD40-induced expression of VEGF (arrow 3). In addition, following activation with a dominant active construct of Akt, we found that a pharmacological mTOR inhibitor did not block VEGF expression. Rather, inhibition of mTORC1 via knockdown of raptor resulted in an increased phosphorylation of Akt (arrow 4) and an increase in endogenous expression of VEGF (arrow 5). Our data provide for a model in which mTORC1 activity provides negative feedback for endogenous VEGF expression, but CD40-inducible expression is dependent on mTORC2-Akt signaling.