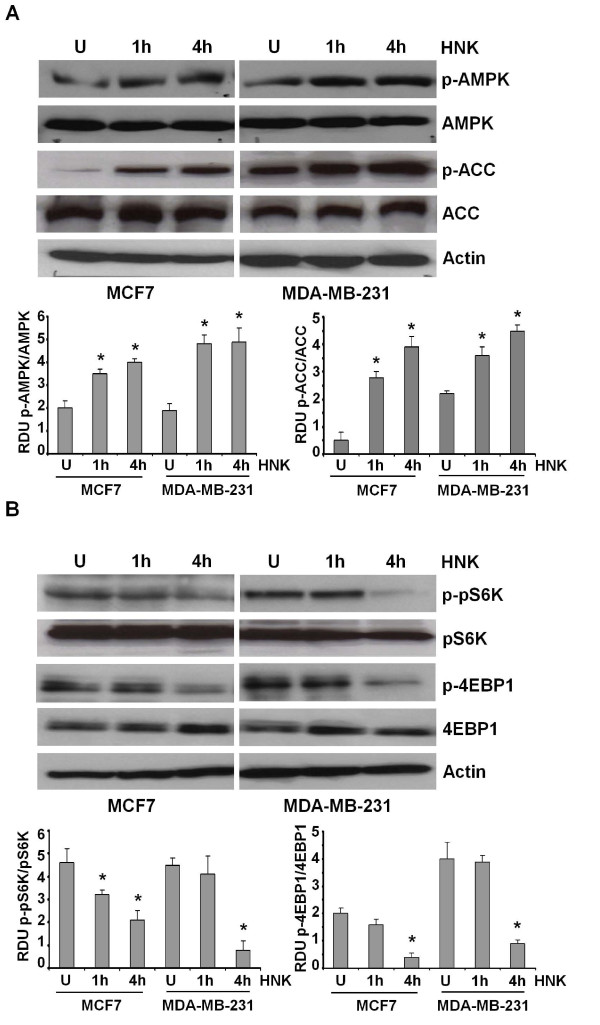
Figure 3.
Honokiol activates AMPK and inhibits pS6K and 4EBP1 phosphorylation in breast cancer cells. (a) MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with honokiol (HNK, 2.5 μM) for indicated time intervals. U, untreated cells. Total protein was isolated, and equal amounts of proteins were resolved with SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblot analysis by using specific antibodies for phosphorylated AMPK (pAMPK-Thr 172) and phosphorylated ACC (pACC). The membranes were reblotted by using total AMPK and ACC antibodies as controls. The blots are representative of multiple independent experiments. The histogram is the mean of densitometric analysis showing relative density units (RDUs) of the Western blot signal for pAMPK and pACC normalized to total AMPK or ACC in three separate experiments. *P < 0.005, compared with untreated controls. (b) Breast cancer cells were treated with honokiol as in (a) and subjected to immunoblot analysis by using specific antibodies for phosphorylated pS6K (p-pS6K) and phosphorylated 4EBP1 (p-4EBP1). The membranes were reblotted by using total pS6K and p-4EBP1 antibodies as controls. The blots are representative of multiple independent experiments. The histogram is the mean of densitometric analysis showing relative density units (RDUs) of the Western blot signal for p-pS6K and p-4EBP1 normalized to total pS6K or 4EBP1 in three separate experiments. *P < 0.001, compared with untreated controls.