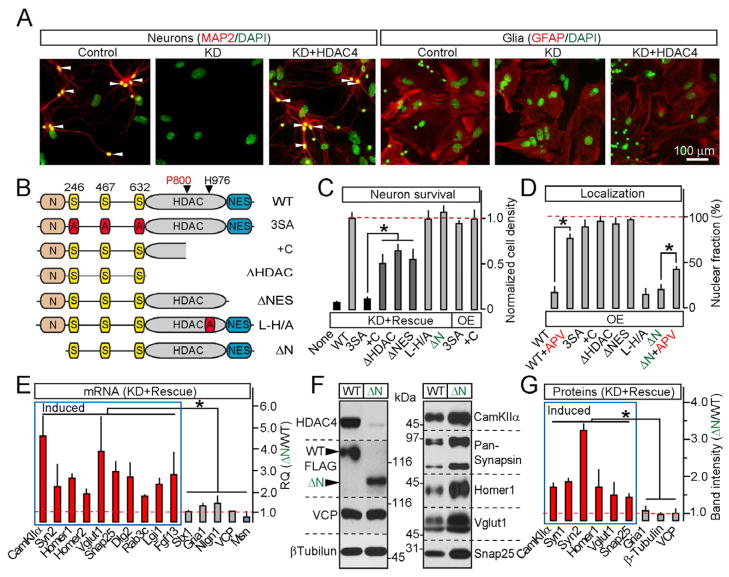
Figure 4. HDAC4 represses transcription and promotes neuronal survival via distinct mechanisms.
A–D, Structure-function analysis of HDAC4-mediated neuroprotection. Cortical cultures were infected at 5 DIV with lentiviruses encoding shRNA against HDAC4 alone (KD) or shRNA together with shRNA-insensitive FLAG-tagged rescue HDAC4 cDNAs. Neuronal survival was analyzed as described in Figure S2A. A, Cell death induced by HDAC4 KD is fully rescued with wildtype HDAC4. B, Schematic representation of mutants used for rescue studies. C, Quantification of neuronal survival in cultures expressing either shRNA together with indicated cDNAs (KD+Rescue) or 3SA and +C mutants alone (OE). D, Localization of rescue mutants expressed without shRNA. See Figure S5 for images and additional data.
E–G, HDAC4 N-termini is essential for transcriptional repression. mRNA and protein expression was examined in neurons carrying shRNA and either the wildtype HDAC4 or the ΔN mutant. E, qPCR measurements of mRNA levels of HDAC4-dependent genes (shown in blue and red) and controls. Data are plotted as ΔN/WT RQ ratio. F and G, Representative immunoblots and quantifications of relative levels of indicated proteins.
All measurements were performed in three independent experiments and presented as Mean±S.D. * = p<0.05.