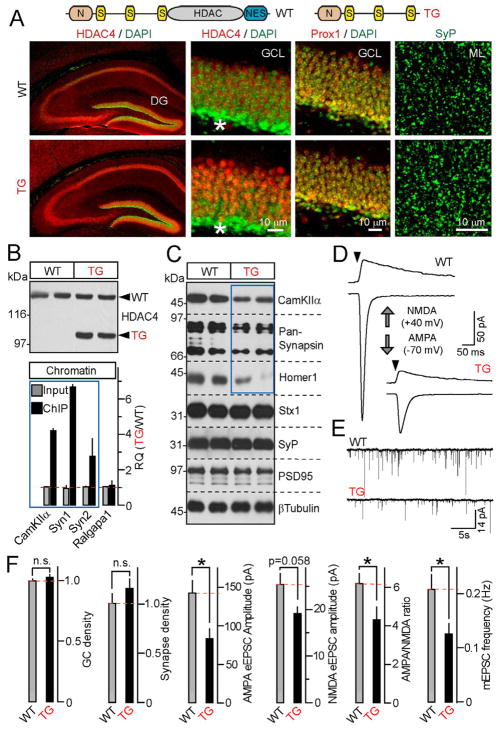
Figure 6. A truncated form of HDAC4 acts as a constitutively nuclear repressor in vivo.
A, Top: Schematic representation of wildtype HDAC4 and a truncated mutant used for the generation of transgenic mice (TG). Bottom: TG accumulates in nuclei and does not influence neuronal density and synapse numbers. Brain sections were labeled with antibodies to HDAC4, Prox1 and SyP. Enlarged images show neuronal somas in the DG granule cell layer (GCL) and synaptic puncta in the molecular layer (ML). Asterisks mark differentiating GCs.
B, TG binds to genomic DNA sites that are occupied by wildtype HDAC4 in an activity-dependent manner. Top: Immunoblot analysis of TG expression in the forebrain. Bottom: Chromatin was co-immunoprecipitated with anti-HDAC4 antibody and analyzed by qPCR with primers specific for HDAC4-interacting sites within CamKIIa, Syn1 and Syn2 genes. Data from three pairs of mice are plotted as TG/WT RQ ratio (Mean±S.D.)
C, TG mice have reduced expression of HDAC4-dependent genes. Proteins extracted from the DG were probed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. Note a selective reduction of CamKIIα, Synapsins 1/2 and Homer1. Data are from two pairs of mice. See Figure S7 for quantifications of protein levels.
D and E, TGs have reduced excitatory synaptic strength. Representative traces of evoked AMPA- and NMDA-type eEPSCs (D) and quantal AMPA-type mEPSCs monitored in acute slices from DG granule cells are shown. Recordings were performed in whole-cell mode in the presence of gabazine.
F, Summaries of synaptic properties of granule cell neurons in the DG of wildtype and TG mice. The densities of Prox1-positive neurons in the GCL and SyP-positive puncta in the ML were normalized to wildtype. All other values are raw. All experiments were performed at postnatal day 25.
Data are plotted as Mean±S.E.M. * = p<0.05. See Table S3B for statistics.