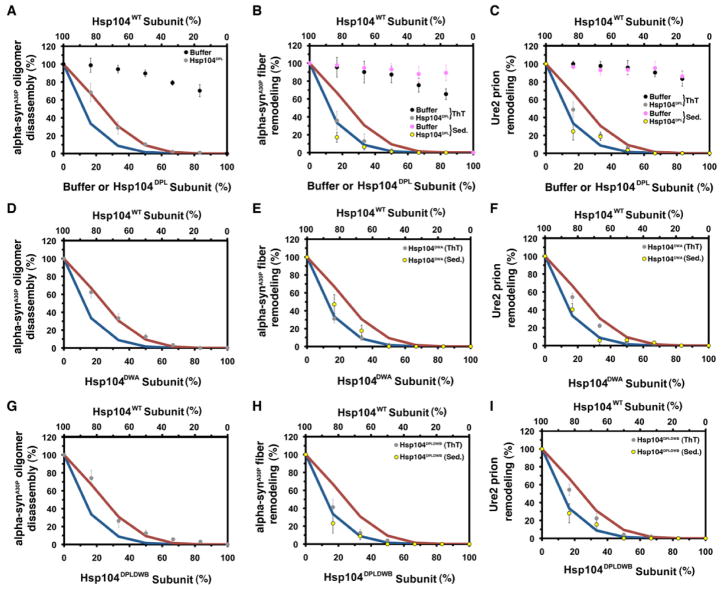
Figure 4. Hsp104 exploits co-operative mechanisms to remodel preamyloid α-synA30P oligomers, α-synA30P amyloids and Ure2 prions.
(A–I) α-synA30P oligomers (A, D, G), α-synA30P amyloid (B, E, H) or Ure2 prions (C, F, I) were treated with Hsp104, Ssa1 and Sis1 plus increasing fractions of buffer (A, B, C), Hsp104DPL (A, B, C), Hsp104DWA (D, E, F) or Hsp104DPLDWB (G, H, I). Oligomer remodeling was assessed by filter trap and amyloid remodeling was assessed by ThT fluorescence (grey or black markers) or sedimentation (purple or yellow markers). Activity was converted to % WT activity. Values represent means±SEM (n=2–4). Expected activity if 1 or more (blue line, A–I), or 2 or more (red line, A–I) mutant subunits ablate hexamer activity.
See also Supplementary Figure S4.