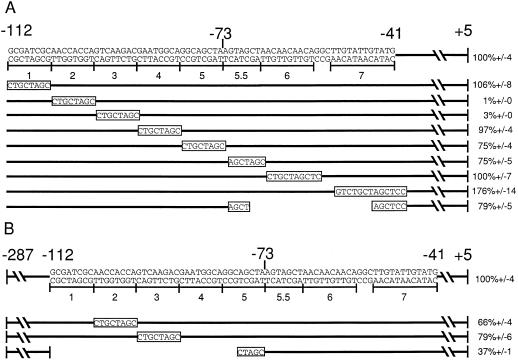
Figure 2.
Activity of a2 promoters with substitution mutations. A, Mutations 1 through 7 were created using PCR to substitute the specific 7- to 13-bp sequence indicated. These mutations maintain the spacing found in the wild-type a2 promoter. The sequence of each of these mutations is shown in the bar below its corresponding number. The last line represents a deletion, with the gap corresponding to the deleted bp. Each of these mutations was assayed for its ability to be activated by C1 and B in the context of the −112-bp promoter. The percentage activation of each of these promoters in transient expression assays relative to the level of activation of the wild-type −112-bp a2 promoter (set at 100%) is shown at the right. Error bars represent se; n = 12. B, Mutations 2 and 3, as well as the deletion shown, were tested in the context of the −287-bp a2 promoter. The percentage activation relative to the −287-bp a2 promoter (set at 100%) is shown at the right. se is indicated for each construct; n = 12.