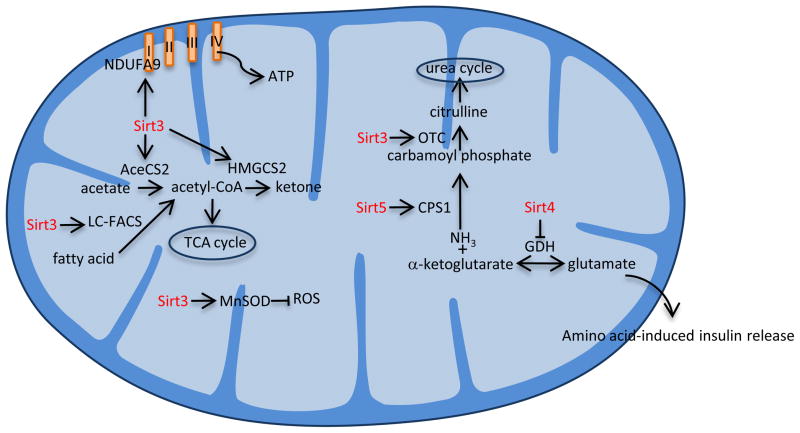
Figure 4.
Mitochondrial function of sirtuins. Sirt3 deacetylates and activates acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 (AceCS2) and long chain fatty acyl-CoA (LC-FACS), which convert acetate and fatty acid, respectively, into acetyl-CoA. It also activates 3-hydroxy-3methylglutaryl CoA synthase 2 (HMGCS2), which is involved in ketogenesis; ornithine transcarbamoylase (OTC), which is involved in the urea cycle; manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), which inhibits reactive oxygen species (ROS) production; and NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 9 (NDUFA9), which a subunit of complex I in the electron transport chain. Sirt4 inhibits glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), which is involved in the synthesis of glutamate and amino acid-induced insulin release, while Sirt5 is also involved in the urea cycle through activating carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1 (CPS1).