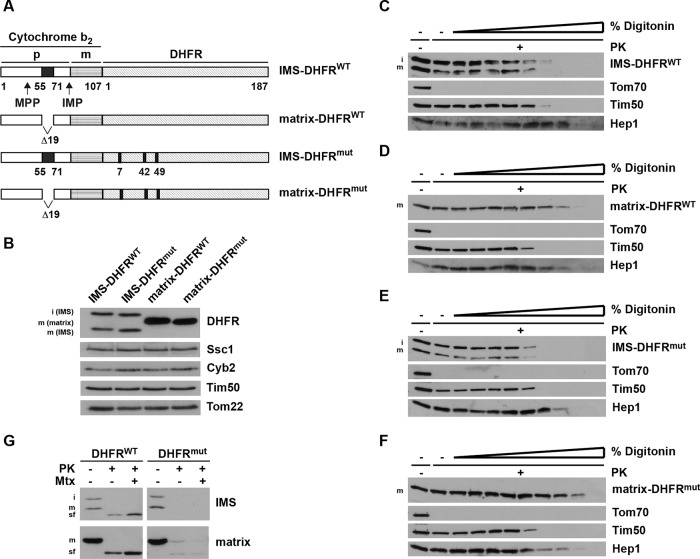
FIGURE 1:
Generation and localization of DHFR constructs in mitochondria. (A) Schematic representation of model substrates. Wild-type and nonfolding mutant versions of mouse DHFR (C7S, S42C, N49C) were fused C-terminally to amino acid residues 1–107 of yeast cytochrome b2, targeting it to the IMS (IMS-DHFR). Constructs with deleted stop-transfer signal are targeted to the matrix (matrix-DHFR). p, bipartite targeting signal of cytochrome b2. Cleavage by the mitochondrial processing peptidase (MPP) leads to the intermediate-sized i-form; cleavage by the IMP leads to the mature m-form. (B) Mitochondria were isolated and analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunodecoration using antibodies against the indicated proteins. DHFR constructs: i-form and m-form. (C–F) Mitochondria were incubated with increasing amounts of digitonin (0.005–0.1%) in the presence of PK for 25 min on ice. Samples were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunodecoration using antibodies against DHFR and the indicated mitochondrial marker proteins (Tom70, outer membrane; Tim50, IMS; Hep1, matrix). (G) Isolated mitochondria were solubilized with Triton X-100 and incubated with PK for 20 min at 0°C in the presence and absence of methotrexate (Mtx). Samples were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunodecoration with antibodies against DHFR. sf, stable fragment upon protease digestion.