FIGURE 8:
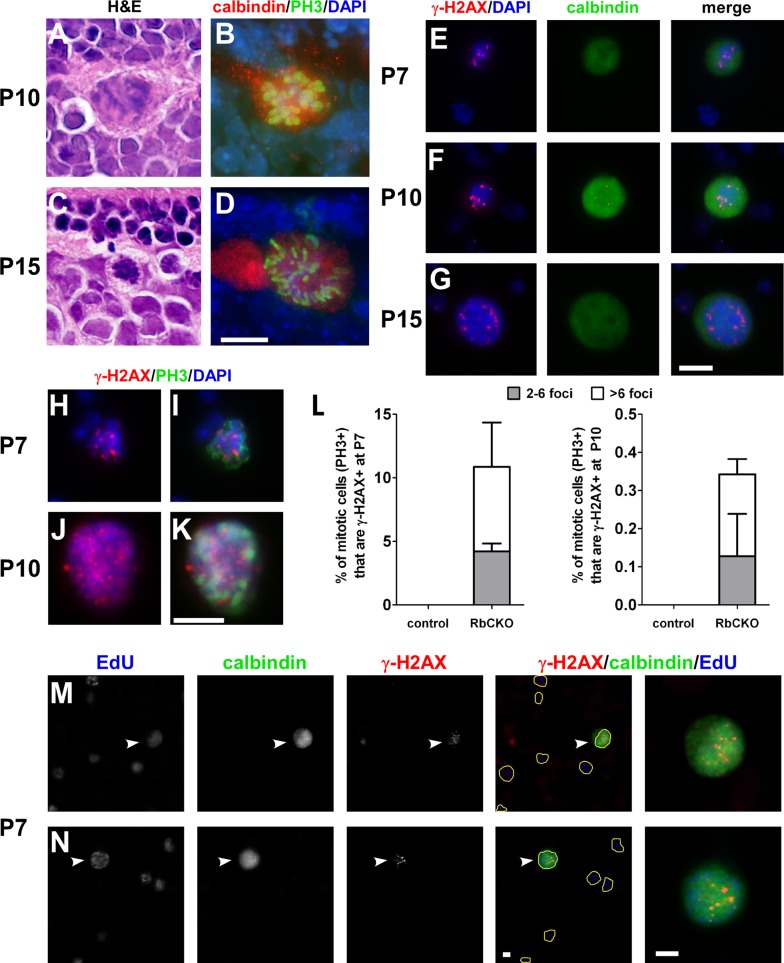
Deregulated cell cycle checkpoint in Rb1-deficient retina. H&E-stained sections show the presence of mitotic figures and condensed chromatin in the outer INL of RbCKO retina at P10 (A) and P15 (C). Sections double labeled with phospho–histone H3 Ser-10 (PH3, green) and calbindin (red) demonstrates that differentiated RbCKO horizontal cells are mitotic at P10 (B) and P15 (D). (E–G) Subset of dissociated RbCKO horizontal cells displays γ-H2AX foci (red) and DAPI (blue) patterns consistent with mitosis at several postnatal ages. (H–K) Dissociated RbCKO retinal cells were colabeled with γ-H2AX (red) and PH3 (green). (L) Quantification of the percentage of mitotic (PH3+) cells that are γ-H2AX+ in control (Six3-Cre+;Rb1lox/+, Rb1lox/+, Rb1lox/lox) and RbCKO at P7 (left) and P10 (right). (M, N) RbCKO horizontal cells labeled with calbindin (white arrowheads, far right) show both markers of genomic instability (γ-H2AX) and DNA synthesis (EdU) after a 4-h in vivo pulse of EdU. EdU+ cells are outlined in yellow in merged images to aid visibility. Shown is the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Scale bars, A–N, 10 μm.