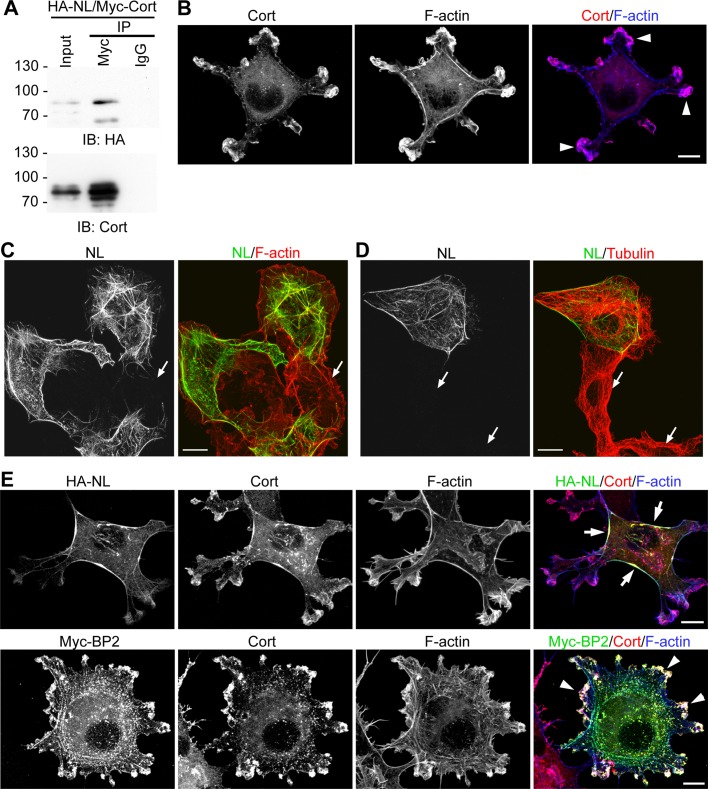
FIGURE 2:
Comparison of the interaction of CTTNBP2NL and CTTNBP2 with cortactin. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation of cortactin and CTTNBP2NL. Whole-cell extracts of COS cells cotransfected with Myc-tagged cortactin (Myc-Cort) and HA-tagged CTTNBP2NL (HA-NL) were precipitated using anti-Myc and nonimmune mouse IgG antibodies. Immunoblotting (IB) was performed to assess the presence of CTTNBP2NL and cortactin in the precipitates. (B) The overlapping distribution of cortactin (Cort) and F-actin at the cell cortex (arrowheads). COS cells were fixed and stained with anti-cortactin and phalloidin (to label F-actin). (C, D) COS cells were transfected with CTTNBP2NL and immunostained with anti-CTTNBP2NL antibody and (C) phalloidin and (D) anti-tubulin antibodies. Arrows indicate the untransfected COS cells, which did not show any obvious immunoreactivity of CTTNBP2NL. (E) CTTNBP2NL preferentially associates with actin stress fibers (arrows), whereas CTTNBP2 colocalizes with cortactin at the cell cortex (arrowheads). COS cells expressing HA-tagged CTTNBP2NL (top) or Myc-tagged CTTNBP2 (Myc-BP2; bottom) were stained with phalloidin, anti-cortactin, and anti-HA or anti-Myc, respectively. Scale bars, 10 μm.