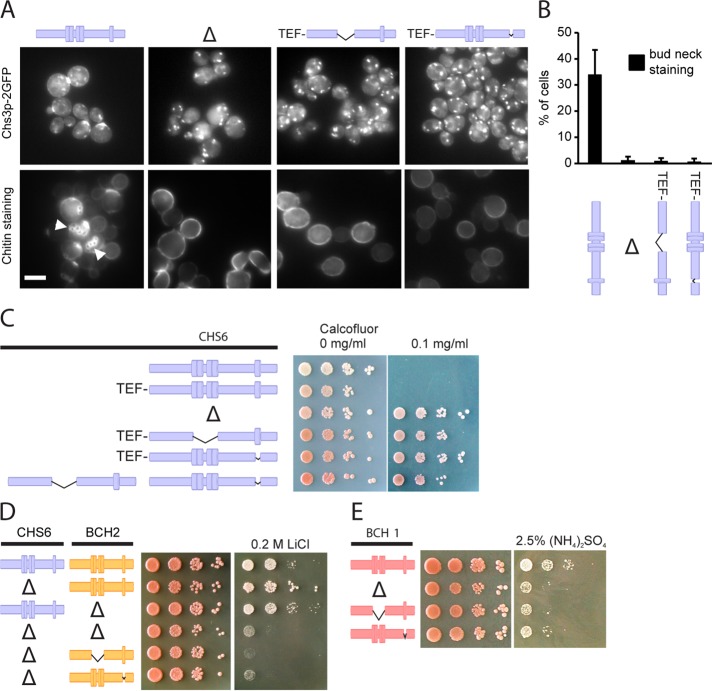
FIGURE 2:
The TPRs are essential for the function of the ChAPs. (A) Chs3p-2GFP localized exclusively to internal structures in Δchs6, Chs6(ΔTPR1-4), and Chs6(ΔTPR5) strains. Accordingly, whereas calcofluor-stained wild-type cells showed bud scar chitin staining (arrowheads), this was absent in the mutants. Scale bar, 5 μm (B) Quantification of results in A. Graph shows an average of three experiments. Bud-neck staining was scored for the entire cell population in at least 100 cells per experiment. Bars, SD. (C) Chs6(ΔTPR1-4) and Chs6(ΔTPR5) strains were resistant to calcofluor. This defect was as pronounced as for a Δchs6 strain. The two mutant alleles showed no cross-complementation. Drop tests: plates were incubated at 30°C for 2–3 d. Blue, Chs6p alleles. Δ refers to Δchs6. (D) Bch2p requires TPRs for functionality. A CHS6 deletion in combination with a Δbch2, Bch2(ΔTPR1-4), or Bch2(ΔTPR5) allele led to lithium sensitivity. Drop tests were performed as described. Yellow, Bch2p alleles. Δ refers to Δchs6 and Δbch2, respectively. (D) Bch1p requires TPRs for functionality. Bch1(ΔTPR1-4) and Bch1(ΔTPR5) cells, like Δbch1, were sensitive to ammonium. Red, Bch1p alleles. Δ refers to Δbch1.