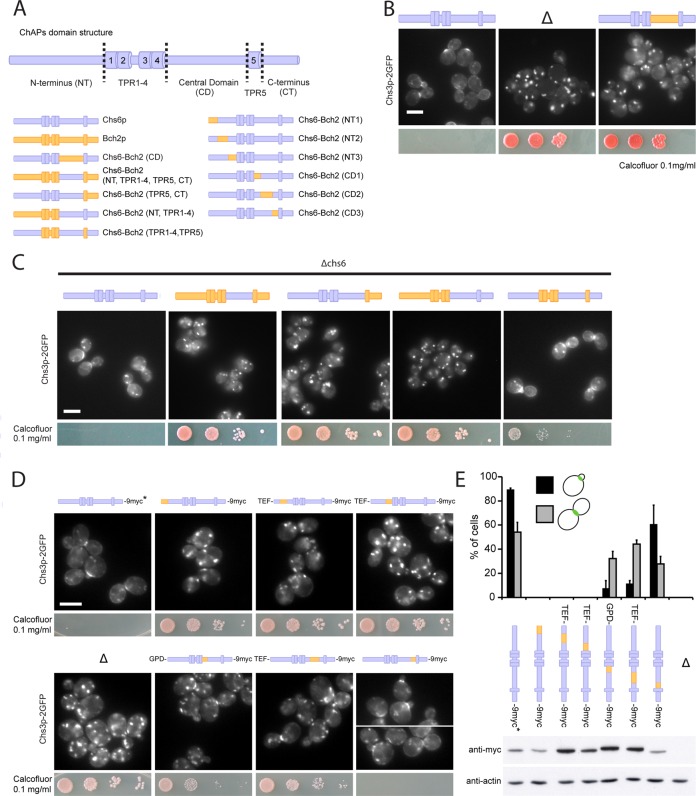
FIGURE 7:
The N-terminus, central domain, and C-terminus of the ChAPs are individually necessary and only together sufficient to convey cargo specificity. (A) Schematic representation of ChAPs domain structure and Chs6p-Bch2p chromosomal chimera constructs. (B) The central domain (CD) of the ChAPs is required for cargo specificity. Chimeric Chs6p bearing the CD of Bch2p was unable to export Chs3p-2GFP and rendered cells calcofluor resistant, like a Δchs6 strain. Chimeras were created by delitto perfetto. Blue, Chs6p domains; yellow, Bch2p domains. Δ refers to Δchs6. Drop assays were performed as in Figure 2. Scale bar, 5 μm. (C) The N-terminus (NT), CD, and C-terminus (CT) are necessary and together sufficient to determine cargo specificity. In a Δchs6 background, calcofluor sensitivity was restored by reintroduction of the CHS6 full-length open reading frame into the BCH2 locus but not by transplantation of the following domains from Chs6p to Bch2p: CD, NT + TPR1–4 + CD, or CD + TPR5 + CT. Transplantation of NT, CD, and CT together restored Chs3p export to the bud neck (by ∼82% compared with wild-type cells). Scale bar, 5 μm. (D) Chs3p bud-neck export requires the entire Chs6p N-terminal domain and the majority of the central domain, the latter only early in the cell cycle. Transplantation of short Bch2p NT fragments into Chs6p resulted in exclusive localization of Chs3-2GFP to internal structures and calcofluor resistance. Transplantation of two short Bch2p CD fragments (aa 409–464 and 465–563), but not the fragment containing aa 564–613, proximal to TPR5 resulted in severely compromised Chs3p cargo export in small-budded cells. Several chimera constructs were expressed chromosomally under the TEF or GPD promoter to achieve protein levels comparable to that of wild-type Chs6p. Drop assays were performed as in Figure 2. Scale bar, 5 μm. (E) Quantification of results in D and expression levels of particular chimera constructs. Graph shows a total of three experiments. Bud-neck staining was scored in 100 small-budded cells (G1/S phase) and 100 large-budded cells (M phase) in each experiment. Bars, SD. Actin serves as a loading control in immunoblot of yeast lysates. Chs6p in wild-type control used in microscopy studies in D and E is untagged, as indicated by the asterisk.