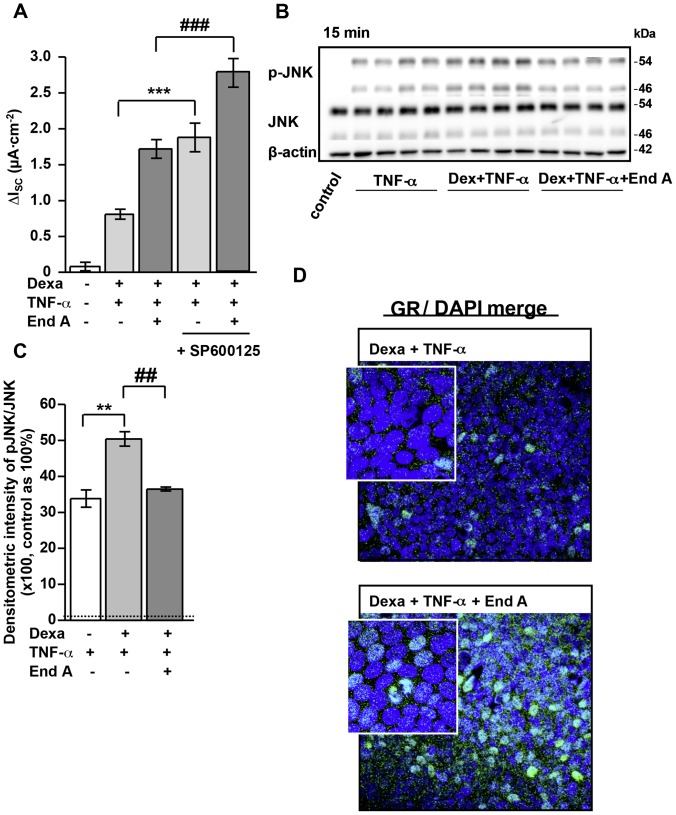
Figure 4. Enhanced nuclear GR translocation through inhibition of TNF-α-induced JNK phosphorylation by endiandrin A in HT-29/B6-GR cells.
(A) HT-29/B6-GR cells were pre-incubated with the JNK inhibitor SP 600125 (10 µM) for 1 hour before addition of dexamethasone (1 µM) and/or TNF-α (500 IU/ml) and/or endiandrin A (20 µM) for 24 hours. Measurement of ENaC-dependent Na+ absorption occurred as the drop in ISC after amiloride (100 µM). Data are given as means ± s.e.m., n = 10, ***P<0.001 compared with dexamethasone + TNF-α 500 IU/ml incubation, ### P<0.001 compared to dexamethasone + TNF-α 500 IU/ml + endiandrin A. (B) Western blot analysis of JNK and pJNK protein (∼46/54 kDa) of HT-29/B6-GR cell lysates incubated with dexamethasone (1 µM) and/or TNF-α (500 IU/ml) w/wo endiandrin A (20 µM) for 15 minutes. Human β-actin (∼42 kDa) served as a loading control. (C) Densitometry of endiandrin A-induced effects on phosphorylated JNK levels normalized to total JNK. HT-29/B6-GR cells were incubated with dexamethasone (1 µM) and/or TNF-α (500 IU/ml) w/wo endiandrin A (20 µM) for 15 minutes. Shown are means ± s.e.m., n = 4, **P<0.01 compared to TNF-α exposure, ## P<0.01 compared to dexamethasone + TNF-α 500 IU/ml. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of GR. HT-29/B6-GR cells were incubated with dexamethasone (1 µM) and TNF-α (500 IU/ml) and/or endiandrin A (20 µM) for 3 hours. Cells were stained with anti-GR antibody (green), nuclei were DAPI stained (blue).